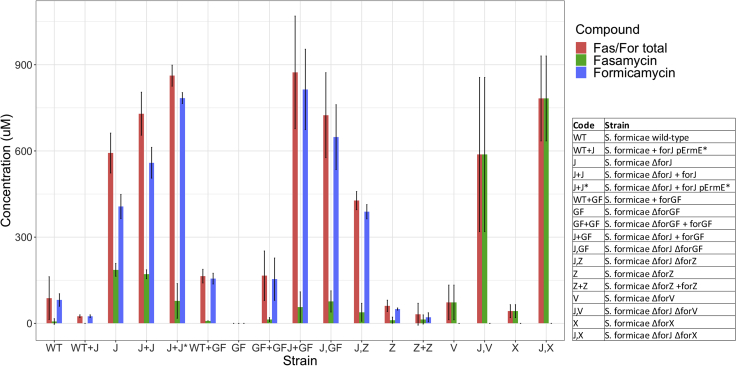
Figure 2.
Manipulation of BGC-situated regulators affects formicamycin biosynthesis during solid culture
Deletion of forJ results in overproduction of formicamycins and accumulation of the fasamycin precursors. Deletion of forGF abolishes fasamycin and formicamycin production. Deletion of forJ combined with a second copy of forGF results in 10-fold higher formicamycin production than the wild-type strain. Deletion of forJ can also be combined with mutations in biosynthetic machinery to generate strains that accumulate precursors and intermediates. Deletion of forZ results in a reduction of formicamycin biosynthesis to around 60% of the wild-type strain on solid agar. Manipulation of forJ is enough to overcome any other regulatory mutation. Error bars represent SD across experimental replicates. Values are mean ± SD; Wild-type, n = 16; mutants, n = 3.