Fig. 5.
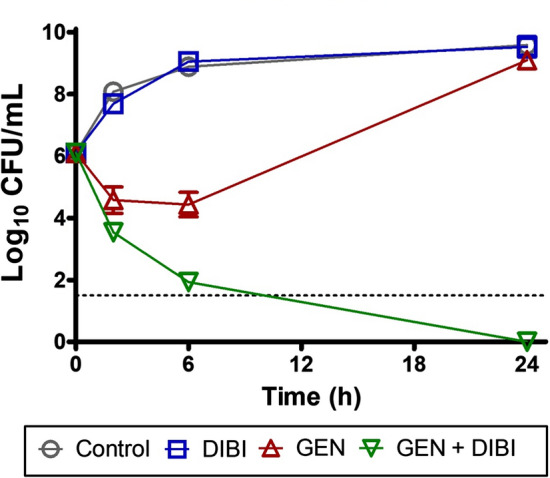
Example of a time kill kinetic assay showing chelator enhancement of antibiotic killing and prevention of survivor re-growth. A. baumannii ATCC 17978 which is sensitive to the aminoglycoside Gentamicin (GEN) (Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) = 1 µg/mL) was exposed to 0.5 µg/mL GEN (i.e., 1/2 MIC) and this caused only partial killing of the population followed by rapid recovery growth that reached near untreated control Colony Forming Units (CFU) levels by 24 h of exposure. The DIBI concentration used in this experiment was 20 µg/mL and this on its own did not affect total CFU by 24 h. It should be noted that a large rapidly growing iron replete bacterial population had been introduced at 0 h and gross effects of DIBI on bacterial numbers would not be expected under these test conditions. However, this DIBI treatment exhibited effects of iron withdrawal as evident when DIBI was applied in combination with GEN. The GEN/DIBI combination resulted in extensive and continued bacterial killing with no detectable CFU remaining at 24 h exposure (results
adapted from Parquet et al. 2019)
