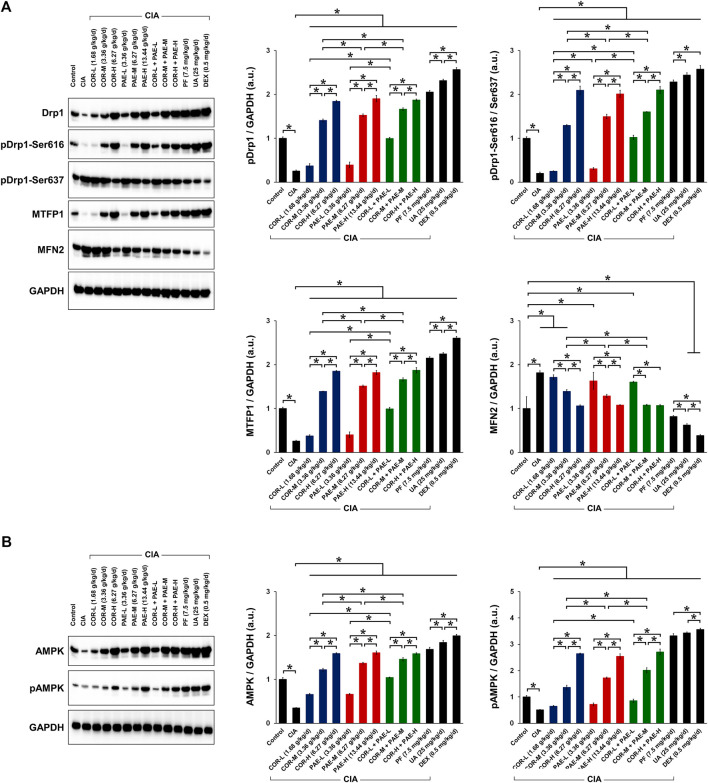
FIGURE 5.
Effect of drug treatment on the expression of proteins associated with mitochondrial function and AMPK signaling in CIA-induced rats. Sprague-Dawley rats were induced by CIA for 14 days and subjected to daily drug administration at various doses for 20 consecutive days. (A) Western blot detection and quantification of the expression of mitochondrial function-related proteins (Drp1, Drp1 phosphorylation at Ser616 and Ser637, MTFP1, and MFN2) in synovial tissues. (B) Western blot detection and quantification of the expression of AMPK in its non-phosphorylated and phosphorylated form in synovial tissues. All protein expression was normalized to that of GAPDH as a housekeeping control. All data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). *p < 0.05. Low, medium, and high doses of COR and PAE were administered, and dose response was analyzed. CIA: collagen-induced arthritis; COR: Cornus officinalis; PAE: Paeonia lactiflora; PF: paeoniflorin; UA: ursolic acid; DEX: dexamethasone; Drp1: dynamin-related protein 1; MTFN1: mitochondrial fission process protein 1; MFN2: mitofusin 2; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.