Figure 6.
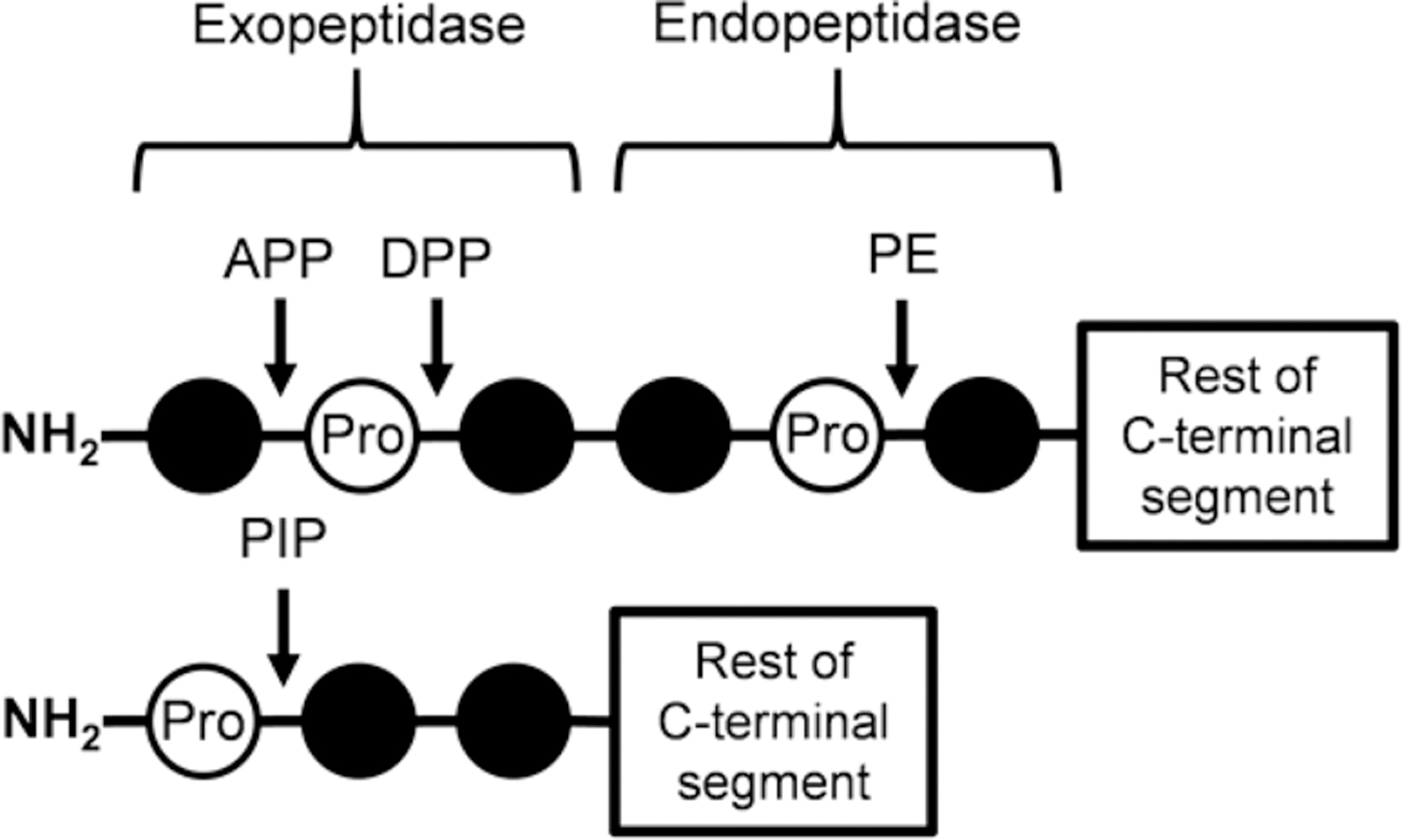
Schematic of cleavage positions for proline-specific peptidases. This shows the general cleavage sites for proline-specific peptidases on a peptide with a free N-terminus. DPPs have the highest cleavage efficiency when removing dipeptides from sequences as shown; however, they can also cleave tri- and tetrapeptides on the carboxyl side of proline residues at a reduced efficiency. PIP prefers to cleave a single proline residue off sequences but can cleave di- and tripeptides on the carboxyl side of prolines at reduced efficiency as well. APP is responsible for the removal of a single residue on the amino side of proline. APP: aminopeptidase P, DPP: dipeptidyl peptidase, PE: prolyl endopeptidase, PIP: proline iminopeptidase.
