Figure 3.
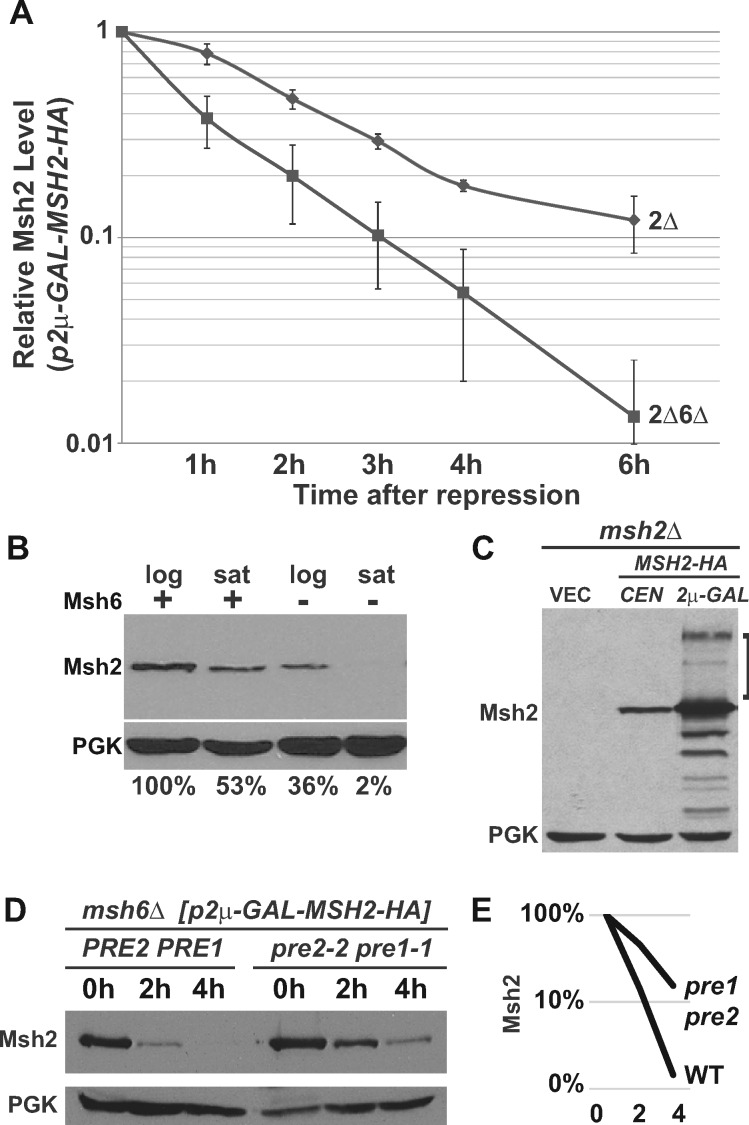
Wild-type Msh2 is degraded more rapidly in the absence of Msh6 via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Indicated msh2Δ (2Δ) or msh2Δmsh6Δ (2Δ6Δ) cells bearing the vector pRS413 (VEC), a centromere-based plasmid encoding MSH2-HA (pCEN-MSH2-HA), or a high-copy plasmid expressing MSH2 under GAL promoter (p2μ-GAL-MSH2-HA) were grown to exponential phase. Protein extracts of ∼3 × 107 cells were subjected to chemiluminescence immunoblotting methods to detect Msh2 with α-HA and a loading control (PGK) with α-PGK. (A) Msh2 has an increased turnover rate in the absence of Msh6. Indicated cells carrying p2μ-GAL-MSH2-HA were grown to exponential phase in medium containing 2% raffinose. MSH2 expression was induced with 2% galactose and repressed with 2% glucose (zero-time point) and time points were taken as described in Materials & Methods. The graph represents the average of three experiments. The data were normalized to the zero-time point. The error bars are the standard error of the mean. (B) The stabilizing effect of Msh6 on Msh2 is more pronounced when cultures become saturated. Strains that were wild-type (+) or lacking Msh6 (–) were grown in synthetic medium to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.6 representing logarithmic phase (log) or until the cultures saturated in stationary phase (sat) at an OD600 of 1.6. Samples were prepared for immunoblotting to detect Msh2 and the PGK loading control. Band intensities of Msh2 were normalized to the loading controls using ImageJ and shown below the immunoblot images as the percentage Msh2 expressed in the presence of Msh6 during logarithmic phase. (C) High molecular weight species of wild-type Msh2 are observed when Msh2 is overexpressed. Indicated cells were grown to exponential phase in 2% galactose to overexpress MSH2. High molecular weight Msh2-HA species are indicated with a square bracket. (D) Genetic inhibition of the proteasome stabilizes monomeric Msh2. A strain with an MSH6 deletion (msh6Δ) and temperature sensitive mutations in genes for the 20S proteasome (pre1-1 pre2-2) and a msh6Δ strain with a wild-type proteasome (PRE2 PRE1) harbored p2μ-GAL-MSH2-HA and were grown to early exponential phase at 30°C in galactose containing medium. The cells were shifted to 37°C for additional 30 min to deactivate the proteasome in the proteasome mutant strain, and then 2% Glucose was added to repress MSH2 (zero-time point, 0 h). Time points at 2 and 4 h were taken at the indicated time after repression. (E) Band intensities of Msh2 from Panel D were normalized to the loading controls using ImageJ and graphed on a log scale as the percentage Msh2 expressed at 0 h for the strains with a wild-type proteasome (WT) or a defective proteasome (pre1 pre2) over the 0, 2, and 4 h time points.