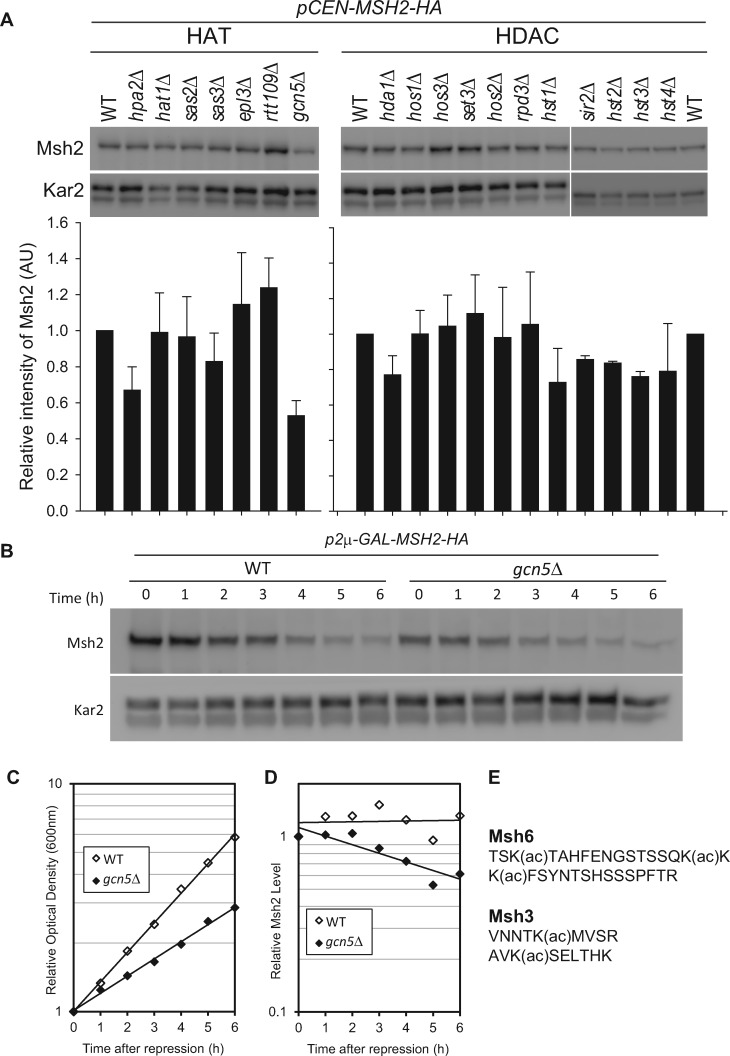
Figure 5.
Gcn5 mediates MutSα turnover through acetylation of Msh6. (A) Msh2 steady-state levels in histone acetyl transferase (HAT) mutants or histone deacetylase (HDAC) mutants. Cells were grown to exponential phase and processed for immunoblotting as described in above. The Msh2 levels from duplicate experiments were quantified, normalized by a loading control Kar2 and graphed as the relative intensity of Msh2 (AU, arbitrary units). Error bars are standard error of the mean. (B-D) Gcn5 regulates the turnover of Msh2. Turnover experiments of Msh2 were conducted in wild-type (WT) or GCN5 deletion strains (gcn5Δ). After MSH2 repression by 2% glucose, cells were harvested and assayed for Msh2 protein levels via immunoblotting (B) and growth via optical density readings (C). Msh2 levels were quantified and normalized to the Kar2 loading control (D). (E) Msh6 and Msh3 acetylated fragments. The acetylation sites were mapped previously (Downey et al. 2015).