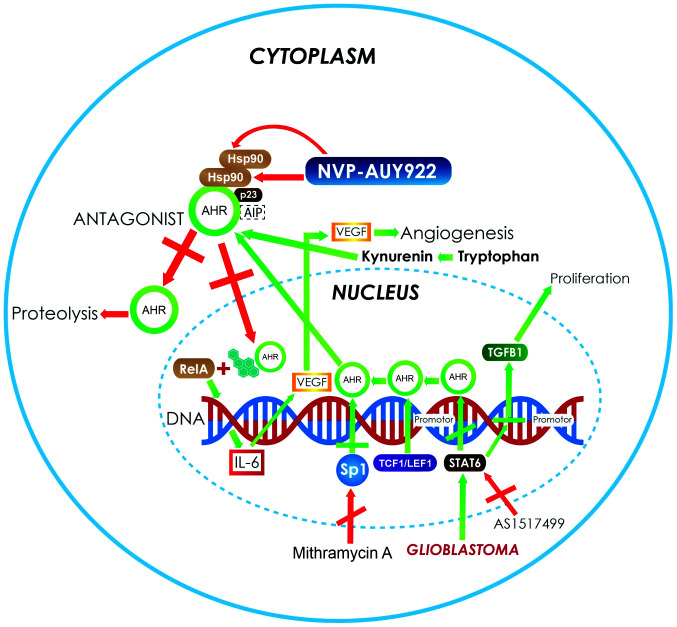
Figure 2.
In astrocytoma and glioblastoma, the activation of the AhR pathway increases the expression of several genes, such as VEGF and TGF-β1 (green arrows) that are involved in angiogenesis and proliferation processes. In addition, the overexpression of Sp1 activates the transcription of AHR, increasing its protein levels. Moreover, there are AHR ligands, such as tryptophan metabolites, produced by the kynurenine pathway in central nervous system tumors such as astrocytoma (green arrows), which also bind and activate the AhR pathway. The strategies used to control the growth of neoplastic cells in astrocytoma and glioblastoma (red arrows) mainly involve the use of AHR antagonist. Another target for therapy is the use of complex-associated protein inhibitors to induce the instability of the receptor. An example of this is NVP-AUY922, which inhibits Hsp90 and induces AHR degradation. Another example is the use of inhibitors such as mithramycin A and AS1517499, which control the autoinduction of AHR protein expression and stop reactive responses. AHR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor A; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-β; Hsp90, heat shock protein 90; Sp1, specificity protein 1; TCF1/LEF1, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor; AIP, AHR-interacting protein; IL, interleukin.