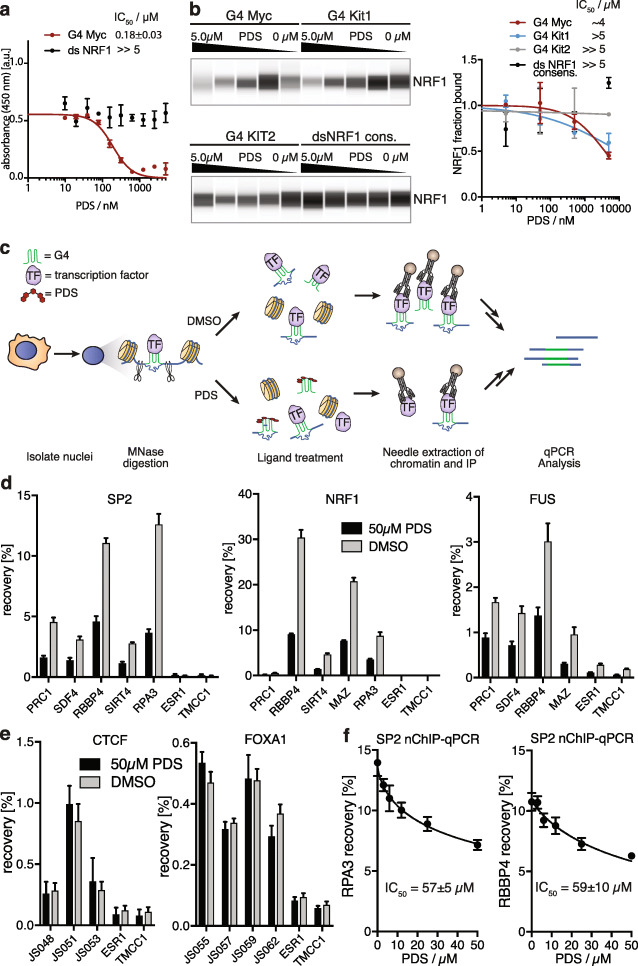
Fig. 3.
Competition of TF binding to G4s in native chromatin by small molecule ligands. a Competition ELISA. Immobilized G4 Myc and a double-stranded DNA consensus oligomer were pre-incubated with increasing concentrations of G4 ligand PDS followed by recombinant FLAG-NRF1 (20 nM) (error bars display standard deviation, N = 3). b PDS dose-dependent competition for NRF1 in K562 cell nuclear lysates. PDS displaces TFs from different G4 oligomers, but does not interfere with binding to the double-stranded DNA consensus oligomer (error bars display standard deviation, N = 2). c Scheme for TF displacement upon G4 ligand treatment and detection via native ChIP. d Native ChIP-qPCR for G4-associated SP2, NRF1, and FUS binding shows a PDS-dependent signal reduction. x-axis, selected positive regions for G4 ChIP-seq and TF ENCODE ChIP signal and two negative control regions (ESR1, TMCC1) with no G4 and TF ChIP-seq signal (error bars display standard error of the mean, N = 4). e Native ChIP-qPCR of control CTCF and FOXA1 are not displaced by PDS (error bars display standard error of the mean, N = 4). f PDS-dependent signal reduction in native SP2 ChIP-qPCR at two positive regions (error bars display standard error of the mean, N = 3)