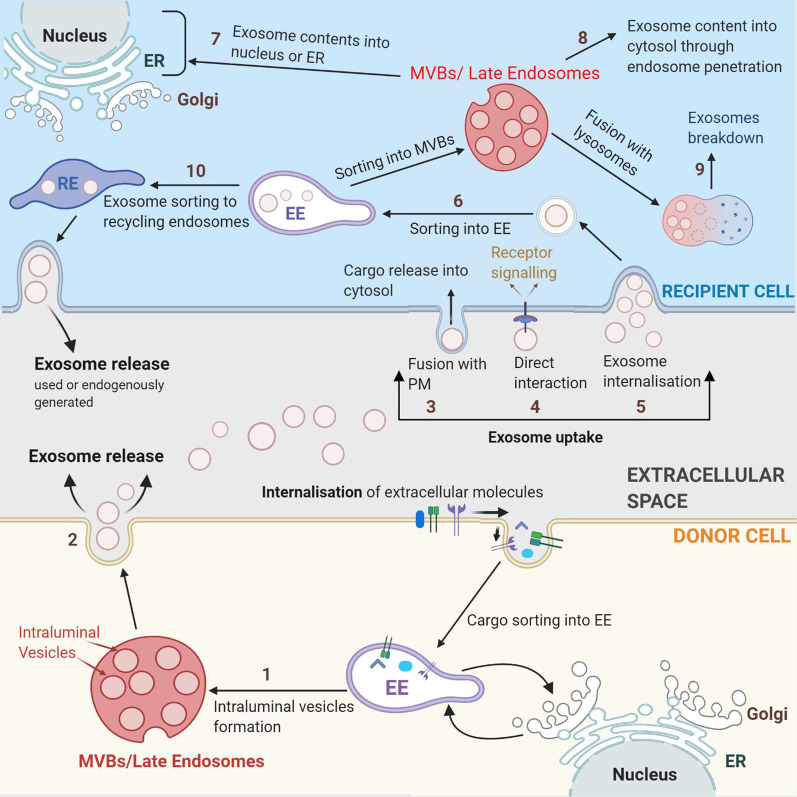
Fig. 6.
Exosome biology. [1] Exosomes are generated through the formation of ILVs in the late endocytic pathway and [2] gets secreted via exocytosis from the plasma membrane. Upon reaching the target recipient cell, [3] exosomes either interact with the surface molecules of recipient cell to induce downstream signalling or [4] fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents into cytosol or [5] get internalised via various routes. [6] Upon internalisation, exosomes are addressed in the early endosome, then late endosomes or MVBs and undergo multiple fates. [7] The exosome contents can get released into the nucleus or ER, [8] leak into cytosol or [9] get degraded in the lysosomes. [10] Another possibility include release back to the extracellular space through the recycling endosome. ILV: Intraluminal Vesicles; EE: Early Endosomes, RE: Recycling endosomes, MVB: Multivesicular Bodies, ER: Endoplasmic Reticulum