Figure 3.
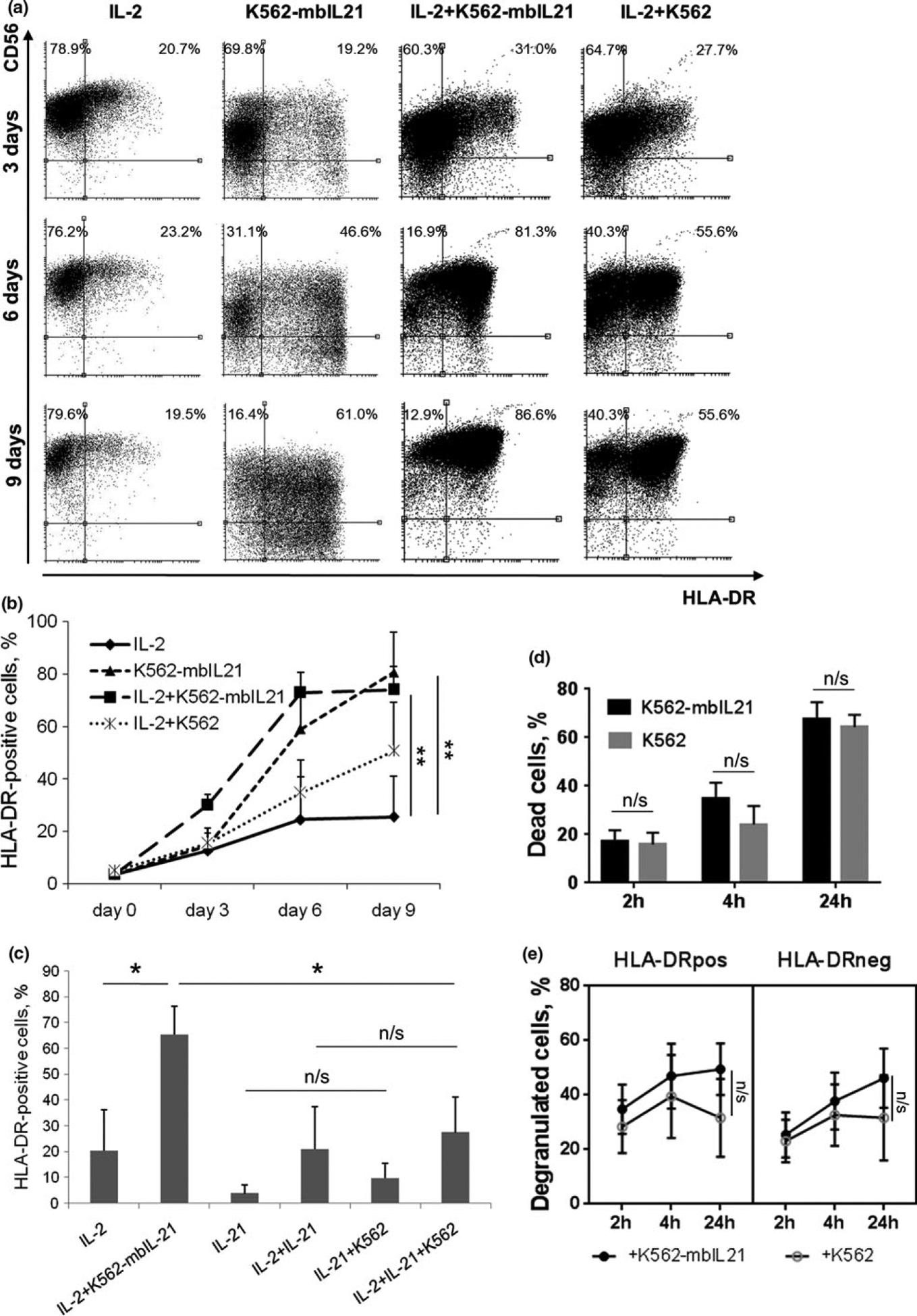
Increase in HLA-DR expression in NK cells upon stimulation with IL-2 and/or K562-mbIL21. (a) HLA-DR and CD56 expression on NK cells after 3, 6 and 9 days of incubation with indicated stimuli. Representative staining of cells from one donor out of three donors examined is shown. (b) Dynamics of HLA-DR expression during incubation with indicated stimuli. Values are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical difference, evaluated by paired t-test, is shown for day 9 time point. (c) Comparison of effects of soluble and membrane-bound IL-21 on HLA-DR surface expression in NK cells analyzed on the 6th day of incubation with indicated stimuli. Values are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical difference was evaluated by paired t-test. (d) Death rate of feeder cells of K562 or K561-mbIL21 cell lines after 2, 4 and 24 h of coincubation with NK cells. Cell death was measured with SytoxRed live/dead stain. Values are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical difference between groups was evaluated by paired t-test. (e) Degranulation of HLA-DR-positive and negative NK cells after 2, 4 and 24 h of coincubation with K562 or K562-mbIL21 feeder cells. Values are mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical difference between groups was evaluated by paired t-test at 24 h time point.
