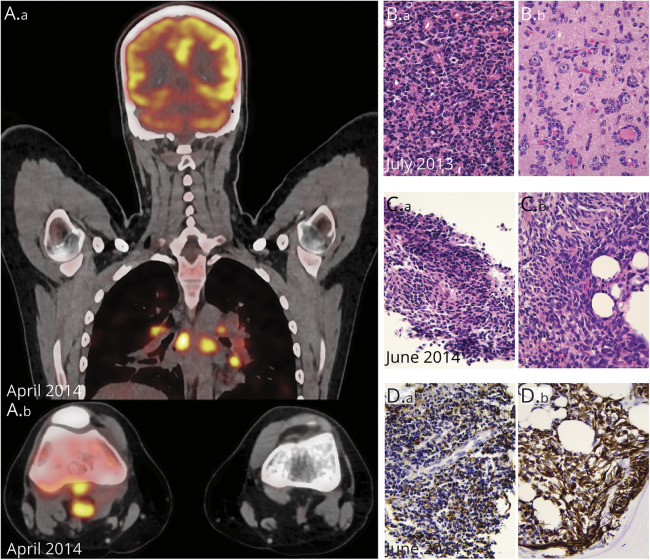
Figure 2. Radiologic and Pathologic Features of the Serially Collected Tumors.
(A, A.a) Whole-body fluorodeoxyglucose PET (FDG PET) imaging with strong FDG uptake in various nodal localizations, notably in the mediastinum. (A.b) Axial plane, FDG PET-CT imaging of both knees; note the hypermetabolic lymphadenopathies behind the right knee. (B) Histology shows a dense, poorly differentiated primary neuroepithelial tumor (B.a, HE 400×), with numerous secondary structures of Scherer (B.b, satellitosis of tumor cells around neurons, HE 400×). (C) Histology of the popliteal fossa lymph node (C.a) and bone (C.b) (HE 400×). (D) Both biopsies show a poorly differentiated neuroepithelial lesion with variable GFAP positivity (400×).