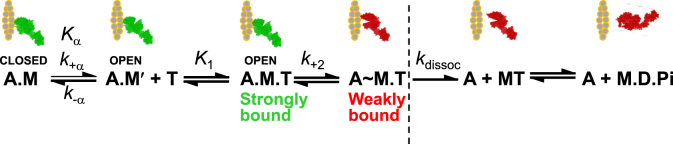
Figure 2.
ATP (T)-induced dissociation of the actin (A)–myosin (M) complex. The strongly bound conformation of the myosin head is shown in green and the weakly bound or detached conformation is shown in red. Kα is the association equilibrium constant for the isomerization of actin–myosin from the closed (A.M) to open (A.M′) conformation of the nucleotide-binding site. K1 (Equation 10) is the association equilibrium constant for ATP binding to myosin that is strongly bound to actin (sometimes referred to as KT), k+2 (Equation 11) is the forward rate constant for isomerization of the collision complex (A.M.T) to the weakly bound ternary complex (A∼M.T), and kdissoc is the rate constant for dissociation of that complex. This paper focuses on the effects of compounds on K1 and k+2 described before the dashed line in the scheme.