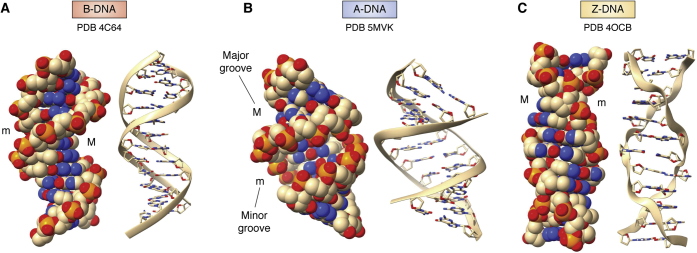
Figure 2.
Crystal structures of B, A, and Z form double helices, each showing space-filling and cartoon representations. Major (M) and minor (m) grooves are indicated.A, the structure of the B-DNA Dickerson-Drew dodecamer (18). The two representations are taken from identical viewpoints, with each showing the narrow minor groove in the top part of the helix and the wide major groove in the lower part. These and all subsequent molecular structure figures have used the ChimeraX molecular graphics program (19). B, representations of an A-DNA dodecamer crystal structure (38), showing an approximately 11-fold helix with the characteristic narrow major groove at the center of the view. Base pairs are tilted with respect to the (vertical) helix axis. Although, even though there are local variations in base and base pair morphological parameters, the overall arrangement is close to an A-DNA helix derived from fiber diffraction. C, representations of the crystal structure of the left-handed Z-DNA sequence d(CGCGCGCGCGCG) (48). Note the characteristic irregular zig-zag feature of the phosphodiester backbone shown in ribbon cartoon form. PDB, Protein Data Bank.