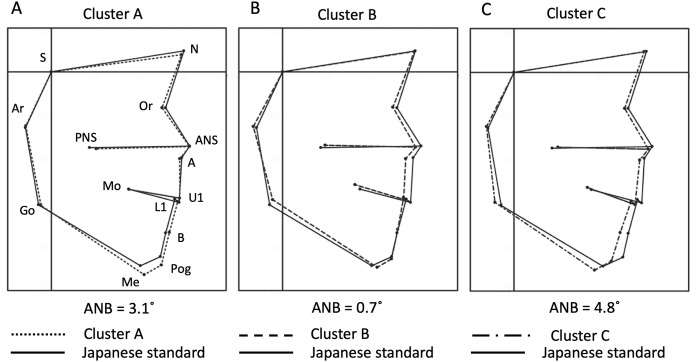
Figure 3. Averaged profilograms of each cluster and their superimposition over the Japanese standard profilogram.
Points S, N, Or, ANS, A, U1, L1, B, Pog, Me, Go, Ar, PNS and Mo were connected on the profilograms to visualise the facial pattern (according to a previous study (Sakamoto, 1959)). The superimposition was performed at point S, parallel to the Frankfurt horizontal (FH) plane. The square dotted line, dashed line, dash-dotted line, and solid line represent clusters A, B, C, and the Japanese standard, respectively. (A) Cluster A exhibited no difference in maxillary position compared to the standard. The mandible and maxilla showed a balanced anteroposterior relationship. (B) Cluster B exhibited significant maxillary retrusion and tendencies towards lingual inclination of the lower incisors, a shorter mandibular ramus, and a larger gonial angle, with crossbite. (C) Cluster C exhibited mandibular and maxillary retrusion, a larger ramus angle, and clockwise rotation of the mandible. The ANB in the averaged profilograms of clusters A, B, and C was +3.1°, +0.7° and +4.8°, respectively. Abscissa: FH-parallel line through S; Ordinate: FH-perpendicular line through S. ANS, anterior nasal spine; A, subspinale; S, sella turcica; N, nasion; Or, orbitale; U1, incisor tip of the most anteriorly placed deciduous maxillary central incisor; L1, lower incisor tip of the most anteriorly placed deciduous mandibular central incisor; B, supramentale; Pog, pogonion; Me, menton; Go, gonion; Ar, articulare; PNS, posterior nasal spine; Mo, mid-point of the deciduous maxillary second molar.