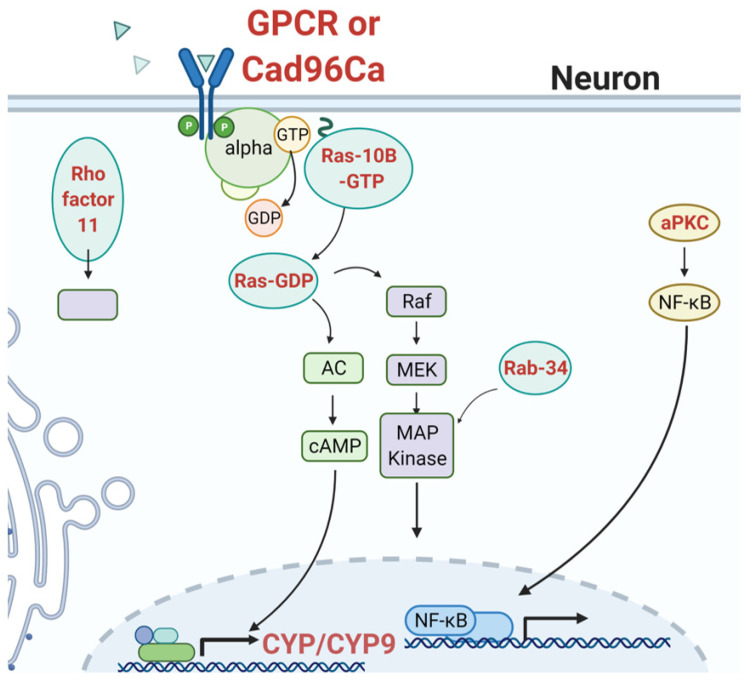
Figure 3.
Signaling mechanisms contribute to pyrethroid resistance. Activation of the signaling mechanism could occur as part of the wound response [118,119,123]. GPCR signaling and subsequent upregulation of detoxification enzyme expression has been described in Culex spp. [34,117]. Increased resistance was observed in the presence of elevated cyclic adenosine-monophosphate (cAMP). Effectors in red font are genetically associated with pyrethroid resistance in natural Ae. aegypti collections from Mexico [31]. Atypical protein kinase C (aPKC), which helps maintain cell polarity, could activate NF-κb upregulation of resistance genes [122]. Figure prepared using Biorender, with permission (Biorender.com, accessed on 22 March 2021).