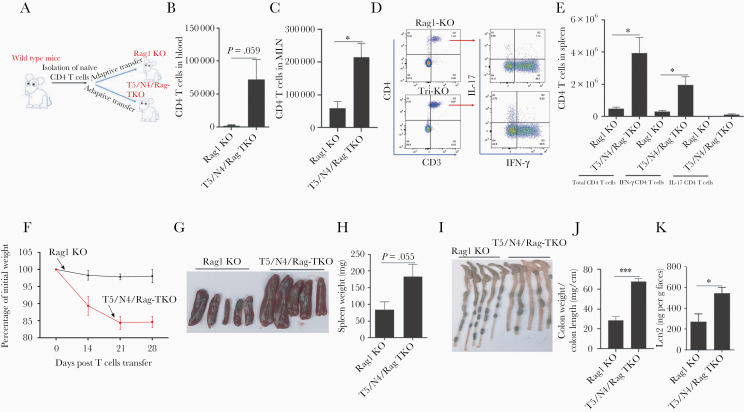
Figure 7.
Deletion of TLR5 and NLRC4 from Rag1-KO mice promotes expansion of exogenously administered effector T cells, thus exacerbating colitis. A and B, Rag1-KO and T5/N4/Rag-TKO mice were intravenously injected with 1 × 106 WT CD45RBhigh CD4+ T cells. B, Peripheral blood levels of CD4 T cells 2 weeks post transfer. C–E, Four weeks post transfer, mice were euthanized enabling assay of total CD4 T cells in mesenteric lymph node and spleen, and analysis of IFN-γ and IL-17–expressing CD4 T cells after stimulating splenocytes with stimulation cocktail. F–K, Development of colitis was assayed by tracking weight loss (F), spleen appearance/mass (G and H), colon appearance (I), colon weight/length ratio (J), and levels of fecal lipocalin-2 (K). Data are means ± SEM, n = 3–5 mice per condition. Abbreviations: IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL-17, interleukin-17; Lcn2, lipocalin-2; MLN, mesenteric lymph node; N4, Nod-like receptor 4; NLRC4, Nod-like receptor 4; T5, Toll-like receptor 5; TKO, triple knockout; TLR5, Toll-like receptor 5; WT, wild type. *P ≤ .05, ***P ≤ .001.