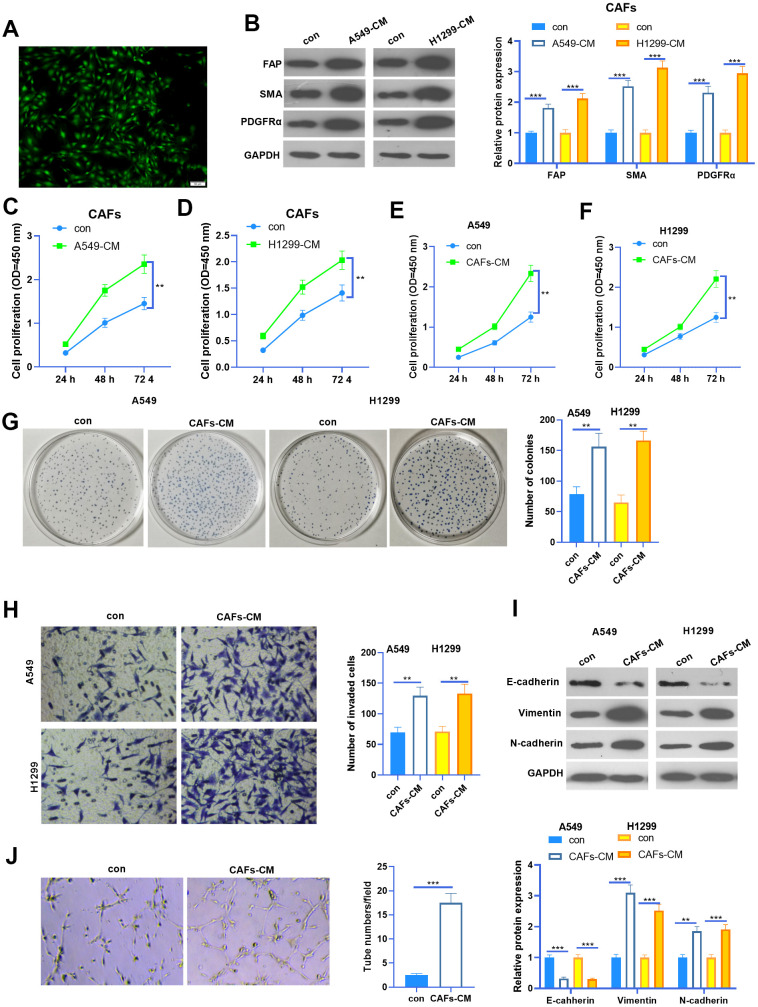
Figure 1.
The interaction between CAF and NSCLC cells. (A) Cellular immunofluorescence (IF) was used to identify CAFs (labeled by SMA). CAFs were co-cultured with NSCLC cell lines (A549 and H1299) or HUVECs for 24 h using Transwell chambers. (B) Western blot was performed to detect the CAF markers, including FAP, SMA and PDGFRα in CAFs. (C, D) CAFs were co-cultured with NSCLC cell lines (A549 and H1299) for different time points (24h, 48h, 72h), and the proliferation of CAFs was determined by the CCK8 assay. (E, F) CAFs were co-cultured with NSCLC cell lines (A549 and H1299) for different time points (24h, 48h, 72h), and the proliferation of NSCLC cells was determined by the CCK8 assay. (G) Colony formation assay was adopted to evaluate the cell colony of NSCLC cells co-cultured with CAFs for 24h, the colonic number was calculated 14 days after incubation. (H) Transwell assay was employed to test the invasive ability of NSCLC cells co-cultured with CAFs for 24h. (I) EMT markers including E-cadherin, Vimentin, and N-cadherin of NSCLC cells co-cultured with CAFs for 24h were determined by western blot. (J) Tube formation assay was implemented to detect the tube formation ability of HUVECs co-cultured with CAFs for 24h. ** represents P<0.01, *** represents P<0.001. N=3.