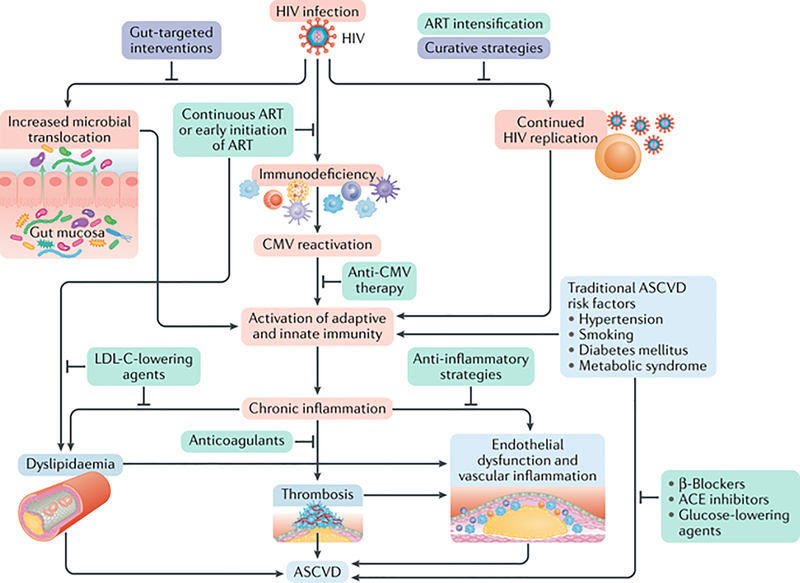
Fig 1. Mechanisms of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease among People Living with HIV.
Mechanisms of ASCVD include HIV infection itself, and the resulting increased microbial translocation, immunodeficiency, Cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation, chronic inflammation and immune activation, dyslipidemia, and traditional risk factors. Pathophysiologic mechanisms are highlighted in red, potential therapeutic targets with supporting evidence in green, and potential future areas of investigation are in purple. Reproduced with permission from Springer Nature.
Source: Hsue PY, Waters DD. HIV infection and coronary heart disease: mechanisms and management. Nature Reviews Cardiology. 2019;16(12):745–759.(13)