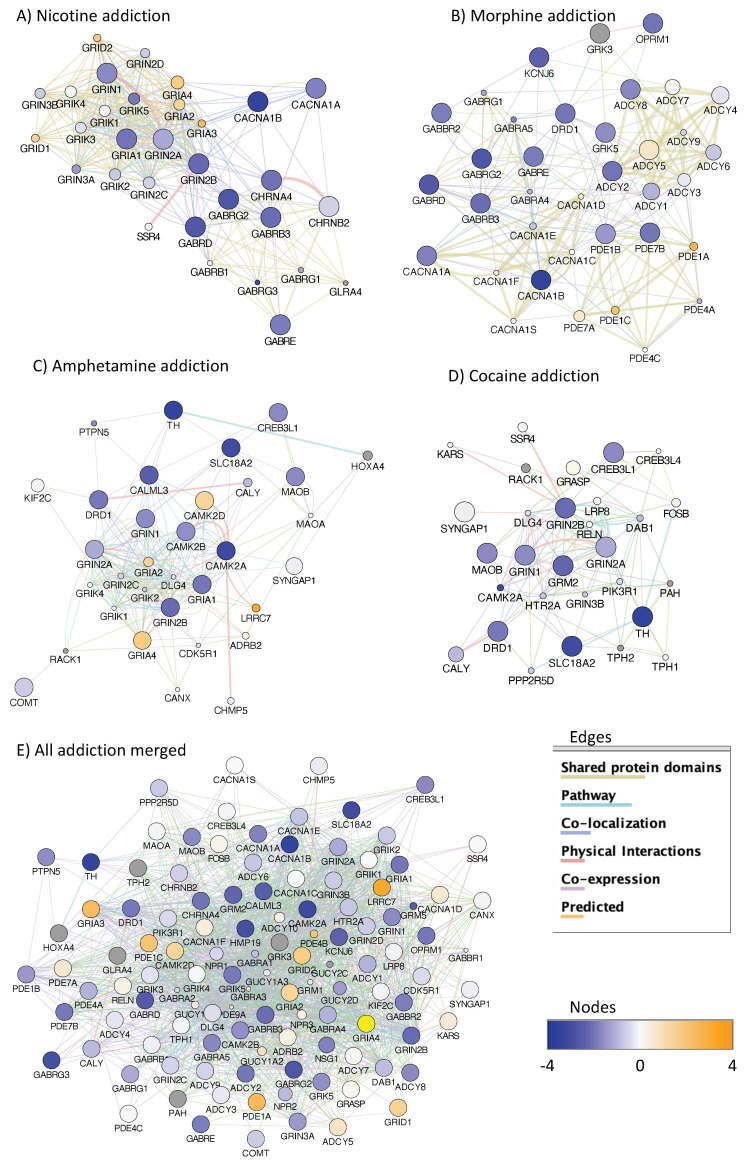
Figure 10.
Gene clusters annotated to drug addiction pathways in HIV+ prefrontal cortex and the effect of Meth use. The analysis of genes with H3K4me3 active regions, including in-gene, downstream distal and proximal, as well as upstream has resulted in gene clusters annotated to addiction. Genes overrepresented in pathways associated to (A) Nicotine addiction (p = 2.2 × 10−5, Benjamini = 7.6 × 10−4), (B) Morphine addiction (p = 1.9 × 10−5, Benjamini = 1.3 × 10−3), (C) Amphetamine addiction (p = 1.4 × 10−4, Benjamini = 6.1 × 10−3) and (D) Cocaine addiction (p = 1.1 × 10−3, Benjamini = 3 × 10−2). (E) These clusters showed a 56% overlap and 100% connectivity in merged features. Node sizes represent connection scores. Blue colors in nodes indicate decrease and orange indicates increase in H3K4me3 peak signals in averaged HIV+Meth+ compared to HIV+Meth- prefrontal cortex specimens. Gray nodes indicate genes in the pathway for which we have not detected any H3K4me3 peak signal. Edge colors represent interaction criteria in connectors as defined in the legend.