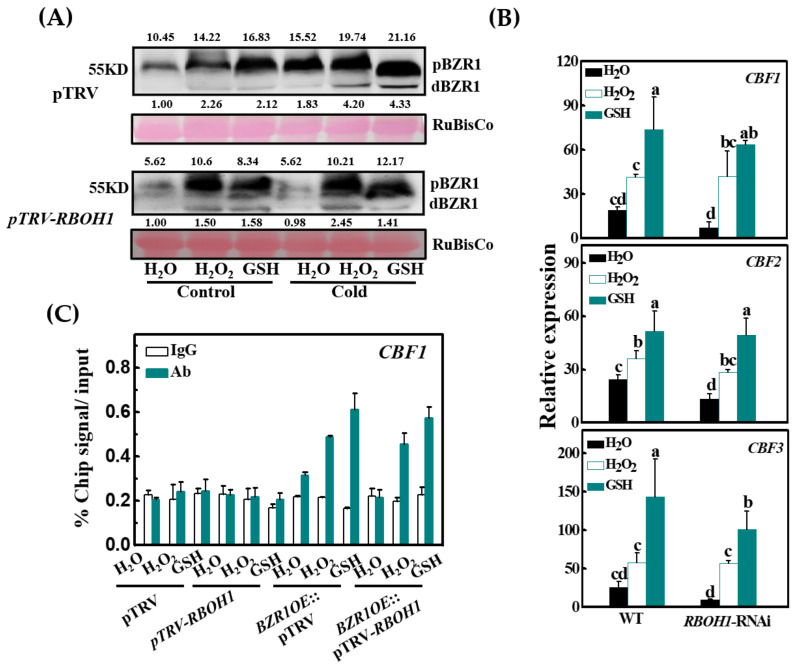
Figure 6.
H2O2 and GSH treatment rescue the accumulation of BZR1 protein and the transcript levels of CBF genes in RBOH1-silenced plants. (A) The accumulation of BZR1 proteins in pTRV and pTRV-RBOH1 plants under control (25 °C) and cold (8 °C) conditions. Plants were foliar applied with distilled water, 5 mM H2O2, and 5 mM GSH, respectively, for 12 h and subsequently exposed to 8 °C for another 12 h, and 35S:BZR1-3HA-overexpressing (BZR1:OE) plants were used for VIGS. The value above and below each lane indicates the relative accumulation of pBZR1 and dBZR1, respectively. (B) The relative expression levels of CBF genes in wild-type (WT) and RBOH1-RNAi plants after exposure to cold at 8 °C for 8 h. Moreover, 12 h before cold treatment, plants were foliar applied with distilled water, 5 mM H2O2, or 5 mM GSH, respectively. (C) ChIP-qPCR analysis showing DNA-binding activity of BZR1 enhanced by H2O2 and GSH treatment in tomato leaves. ChIP was performed with BZR1:OE (pTRV and pTRV-RBOH1) plants foliar applied with H2O, 5 mM H2O2, or 5 mM GSH for 12 h. CBF1 promoter fragments were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody. Mouse IgG was used in control reactions. Input- and ChIP-DNA samples were quantified by qRT-PCR. The ChIP data are shown as % input DNA. Data are the means of three biological replicates (±SD) shown by vertical error bars. Different letters indicate significant differences according to Tukey’s test at 0.05% level. VIGS, virus-induced gene silencing.