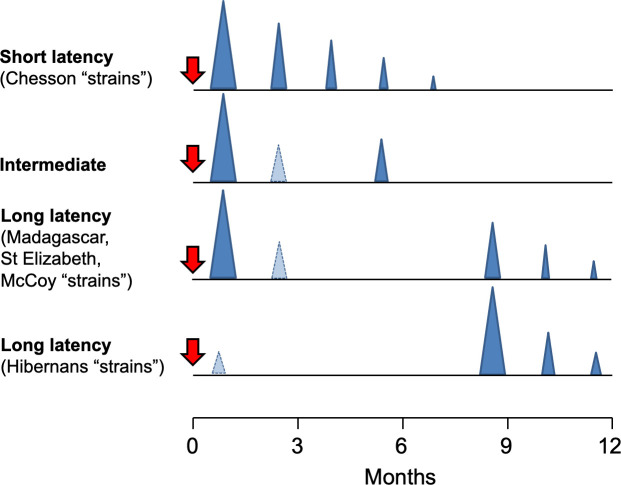
Fig 2. Plasmodium vivax relapse patterns.
The temporal patterns of P. vivax relapse in different “strains.” The red arrow indicates the infective mosquito bite which leads to the primary infection. The blue triangles represent patent P. vivax infections; the largest triangle is the primary infection. The proportions of successive relapses decline, and there is an increasing probability that the relapses are oligosymptomatic or asymptomatic. The translucent blue triangles are P. vivax infections which may sometimes occur. The short latency frequent relapse pattern (typified by the “Chesson strain”) is prevalent across tropical areas. The intermediate phenotype may occur in South Asia. The long latency phenotype (typified by the Madagascar, St Elizabeth, and McCoy strains) is found in Central America, North Africa, and central Asia, while the long latency “hibernans” phenotype, which was prevalent in Northern Europe and Russia, is still found in North Korea.