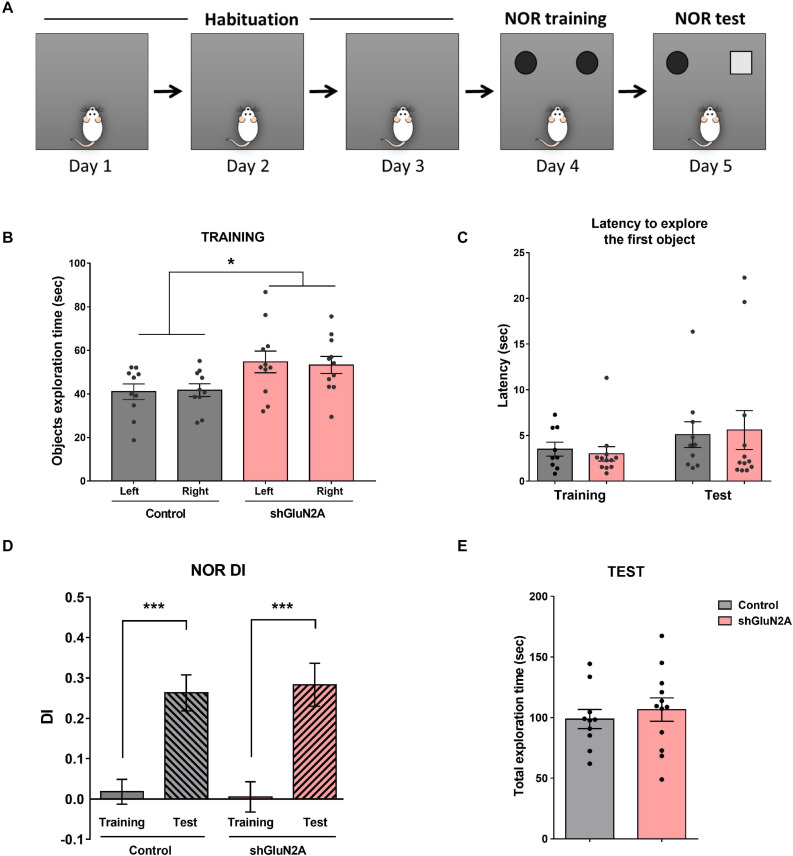
FIGURE 4.
Novel object recognition. (A) Representative scheme of the novel object recognition (NOR) task. Habituation to the arena: three 10-min sessions on consecutive days. NOR training session: rats were exposed to two identical objects for 5 min in the familiar arena. NOR test session: rats were exposed to one familiar and one novel object for 5 min in the arena. (B) Training session: shGluN2A-injected animals showed a significant increase in total object exploration time (*p < 0.05, Two-way ANOVA, Tukey posttest). However, there was no significant difference between exploration of each object in control and shGLUN2A-injected animals. (C) shGluN2A-injected animals showed similar latencies to explore the objects compared to controls during training (p = 0.6478, unpaired t test) and test sessions (p = 0.8527, unpaired t test). (D) NOR test session: discrimination index (DI) at training (plain bars) and test (striped bars) were represented. Both groups of animals reached learning criteria DIte significantly different from DItr (***p < 0.0001, unpaired t test). (E) There was no difference in total object exploration time during the test session between control and shGluN2A-injected animals (p = 0.5494, unpaired t test). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Animals: n = 9 control, n = 11 GluN2A KD.