Figure 3.
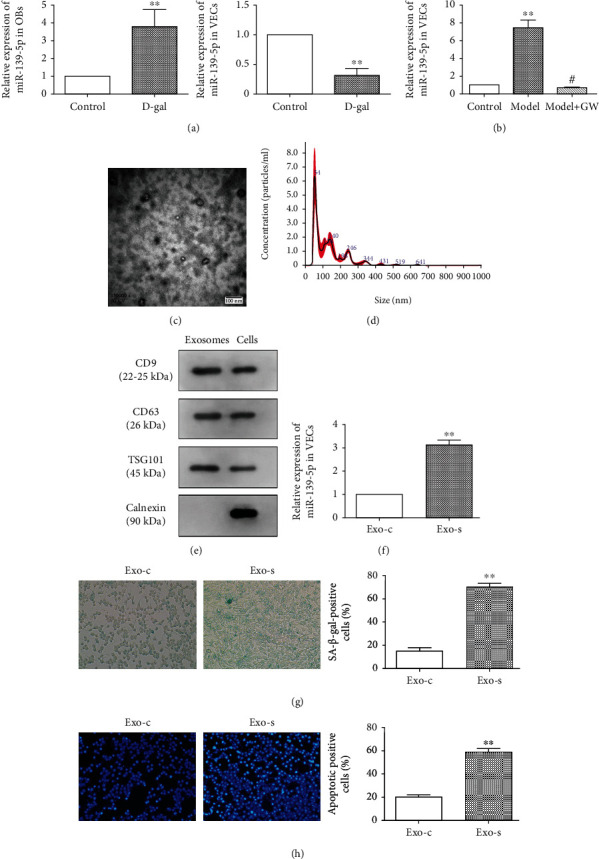
Effect of osteoblast exosome-derived miR-139-5p on the biological function of vascular endothelial cells. (a) Expression of related miRNA in two types of cells treated by D-gal for 48 h. (b) Expression of miR-139-5p in vascular endothelial cells in the coculture system (∗∗ means comparison with the control group, p < 0.01; # means comparison with the model, p < 0.05). (c) Electron microscope scanning of exosome-isolated osteoblast cells and (d) particle size analysis of exosome western blot analysis (e) of exosome-enriched proteins (CD9 (22-25 kDa) and CD63 (26 kDa)) and the key proteins for miRNA function (TSG101 (45 kDa) and calnexin (90 kDa)). (f) Levels of miR-139-5p in exosomes isolated from the control and senescence groups of osteoblast cells were determined by qRT-PCR analysis (∗∗p < 0.01). (g) Senescence staining of vascular endothelial cells by the control and senescence groups of osteoblastic exosomes and quantitative analysis (∗∗p < 0.01). (h) Staining of the control and senescence groups of osteoblastic exosomes on apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells and quantitative analysis (∗∗p < 0.01).
