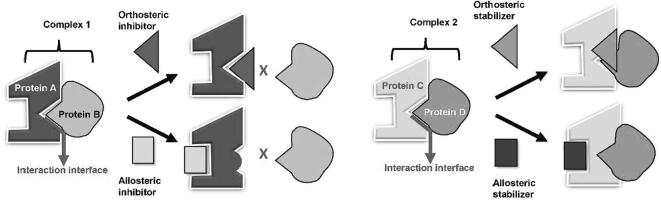
Fig. 1.
Different strategies for designing PPI modulators. Modulation of PPIs can be achieved by using inhibitors or stabilizers to target the orthosteric or allosteric sites of the protein-protein complex. (Right) graphic expression of PPI inhibitors. Protein A binds to Protein B to form Complex 1. Orthosteric inhibitors bind directly to the PPII, which hinders Protein B from binding with Protein A. On the other hand, allosteric inhibitors bind to a region distal from the PPII on Protein A, which induces a conformational change to obstruct Protein B from binding with Protein A. (Left) graphic expression of PPI stabilizers. Protein C interacts with Protein D to form Complex 2. Orthosteric stabilizers bind directly to the PPII, which enhances the binding affinity between Protein C and D. Allosteric stabilizers bind to a region distal to the PPII on protein C, which induces a conformational change to enhance the binding affinity between Protein C and Protein D.