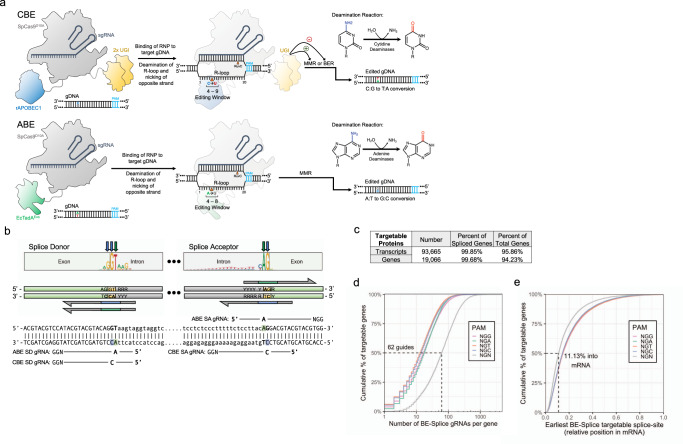
Fig. 1. Overview of the BE-splice approach.
a Generalized base editing mechanisms of CBEs and ABEs. b Positioning of BE-splice sgRNAs within conserved splice-donor and splice-acceptors motif. Logo plots were generated from all human protein coding gene splice sites. Arrows indicate the base targeted by either CBEs (blue), or ABEs (green). c Breakdown of transcripts and genes targetable by BE-splice, showing the vast majority of spliced genes are targetable by this approach (99.68%). d Distribution of BE-splice sgRNA density across each gene. 50% of genes have 62 or more sgRNAs mapping to them when accounting for all PAM identities and both CBE and ABE approaches. e Distribution of the position of the first sgRNA for each gene, with 50% having their first sgRNA 11.13% way through the mRNA or earlier. Source data are available in the Source Data file.