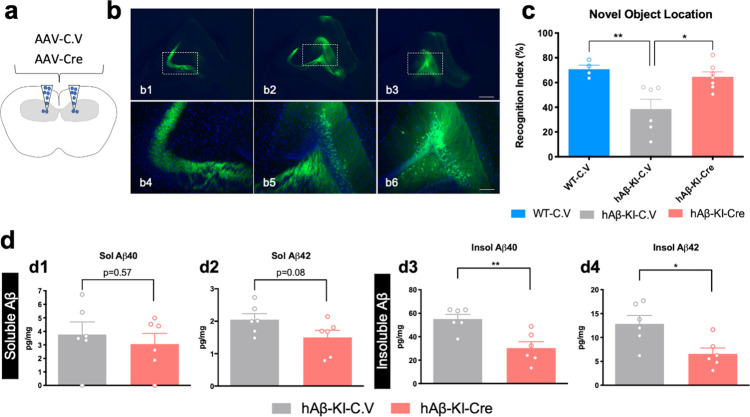
Fig. 6. Cre-mediated deletion of Aβ encoding exon ameliorates the hippocampal memory deficits in hAβ-KI mice.
a Schematic diagram of AAV delivery in the hippocampus (coronal section). b Representative images of AAV-CAMKII-GFP construct expression in the hippocampus. c Cognitive performance (OLM) of 25-mo WT and hAβ-KI homozygous mice treated with control AAV-CAMKII and experimental AAV-CAMKII-Cre vectors (One-way ANOVA, F2,14 = 5.971; Tukey’s post hoc test, *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01)) (blue = WT-C.V, gray = hAβ-KI-C.V and red = hAβ-KI-Cre). (n = 4 in WT-C.V, n = 6 in hAβ-KI-C.V and n = 7 in hAβ-KI-Cre). d Hippocampal Aβ40 and Aβ42 was quantified by MSD V-PLEX Plus Aβ Peptide Panel 1 (6E10) Kit (n = 6/genotype/treatment) (gray = hAβ-KI-C.V and red = hAβ-KI-Cre), showing a significant decrease in soluble Aβ40 (unpaired, two-tailed t-test, p = 0.057) and Aβ42 (unpaired, two-tailed t-test, p = 0.08) and insoluble Aβ40 (unpaired, two-tailed, t-test **p = 0.0042) and Aβ42 (unpaired, two-tailed t-test, *p = 0.0149) in hAβ-KI-Cre compared to hAβ-KI-C.V mice. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. Scale bar: 400 μm (b1–b3), 100 μm (b4–b6). AAV-CAMKII-GFP construct were defined in the figures as control vector (C.V) and AAV-CAMKII-Cre as Cre.