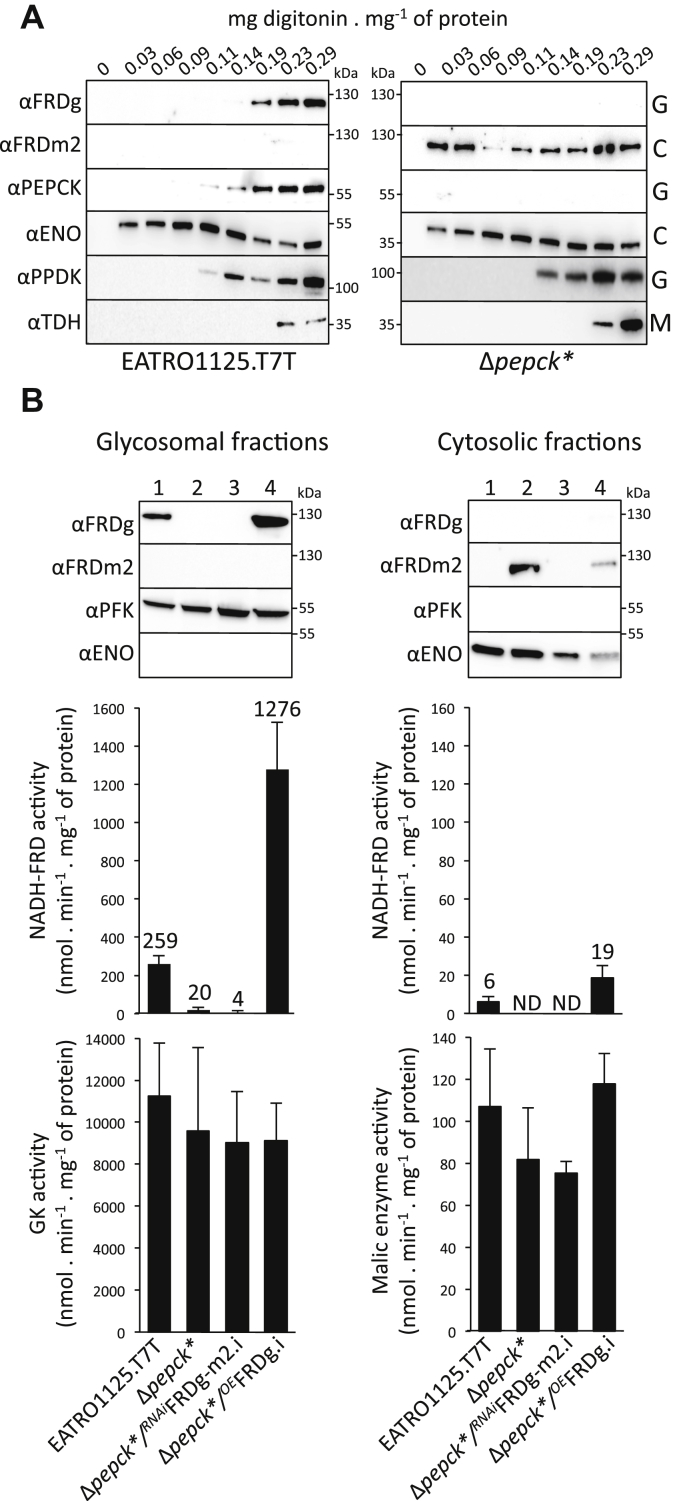
Figure 6.
The cytosolic FRDg-m2 chimeric isoform is not enzymatically active. A, shows the glycosomal and cytosolic localization of FRDg and the chimeric FRDg-m2 isoforms, respectively, by digitonin titration. The supernatant collected from the EATRO1125.T7T and Δpepck∗ cells incubated with 0–0.29 mg of digitonin per mg of protein was analyzed by western blot using the anti-FRDg, anti-FRDm2 as well as immune sera against cytosolic (enolase, αENO), glycosomal (αPPDK), and mitochondrial (threonine dehydrogenase, αTDH) markers. B, shows the western blotting and enzymatic activities determined in the glycosomal and cytosolic fractions of EATRO1125.T7T (1), Δpepck∗ (2), Δpepck∗/RNAiFRDg-m2.i (3), and Δpepck∗/OEFRDg.i (4) cells lines. Expression of FRDg and the chimeric FRDg-m2 isoforms was determined by western blotting using the anti-FRDg and anti-FRDm2 immune sera (top panel). Immune sera against the glycosomal phosphofructokinase (αPFK) and the cytosol enolase (αENO) were used as loading controls. NADH-FRD activity was determined on the same fractions used for western blot analyses (mean of three independent experiments). For normalization, the glycerol kinase (GK) and malic enzyme activities were also determined in the glycosomal and cytosolic fractions (lower panel).