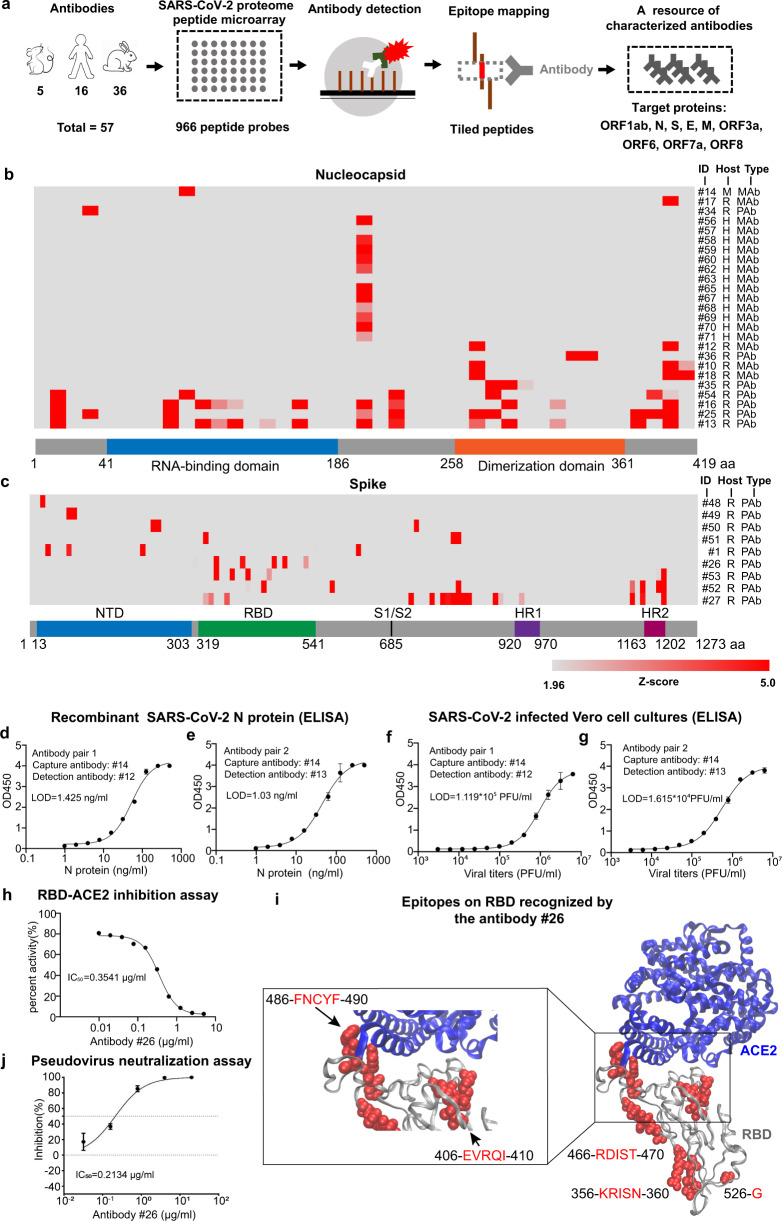
Fig. 1.
The epitope profiling database constructed by using a peptide-based SARS-CoV-2 proteome microarray and its application. a Schematic illustration of epitope mapping using a peptide-based SARS-CoV-2 proteome microarray. b, c Distribution of antibody epitopes within the N and S proteins respectively. The x-axis represents the protein sequence. The y-axis represents the identification (ID) number (#number), host (mouse = M, rabbit = R, human = H) and clonality of the antibody (polyclonal antibody = PAb, monoclonal antibody = MAb). d, e Detection of the purified, full-length recombinant N protein using ELISA prepared with two antibody pairs selected from epitope mapping analyses. f, g Detection of the N protein from inactivated SARS-CoV-2 in cell culture using ELISA prepared with two antibody pairs selected from epitope mapping analyses. h The neutralization activity of antibody #26 using an S-RBD-ACE2 inhibition assay. i Structural analysis of the antibody #26 epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 RBD (PDB ID: 6m0j). j Neutralization activities of antibody #26 using a pseudovirus assay