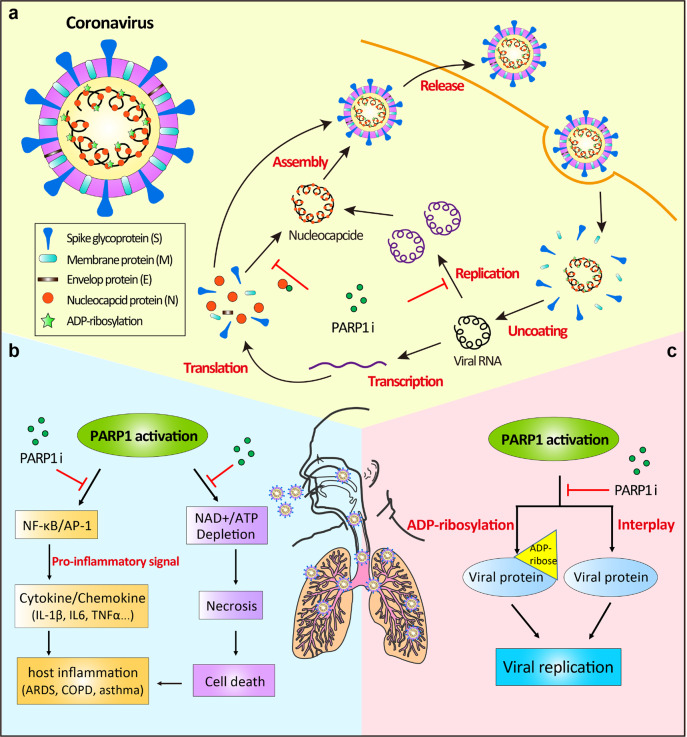
Fig. 5.
The putative mechanisms for CVL218 as a PARP1 inhibitor to combat the COVID-19 disease, derived based on the data present in this study and the known antiviral activities of PARP1 inhibitors previously reported in the literature. a Schematic diagram showing the possible antiviral mechanisms of PARP1 inhibitors in the life cycle of coronavirus in human cells. PARP1 inhibitors have been previously reported in the literature to suppress viral replication and imped the binding of nucleocapsid protein to viral RNAs, thus preventing the virus infection.47–50 b Potential protective effects of PARP1 inhibitors in the treatment of COVID-19. The anti-inflammation effects of PARP1 inhibitors may be achieved through two possible molecular pathways. The first one is to modulate the expression of pro-inflammation factors such as NF-κB, AP-1, IL-6 and downstream cytokines and chemokines.51–54 The second possible pathway is to prevent the overactivation of PARP1 and thus avoid the depletion of NAD+ and ATP, and the consequent cellular energy failure and cell death caused by necrosis.51–54 c The potential antiviral effects of PARP1 inhibitors through suppressing the ADP-ribosylation of viral proteins and intervening the host-pathogen interactions, thus resulting in the inhibition of viral replication48,49,56,57