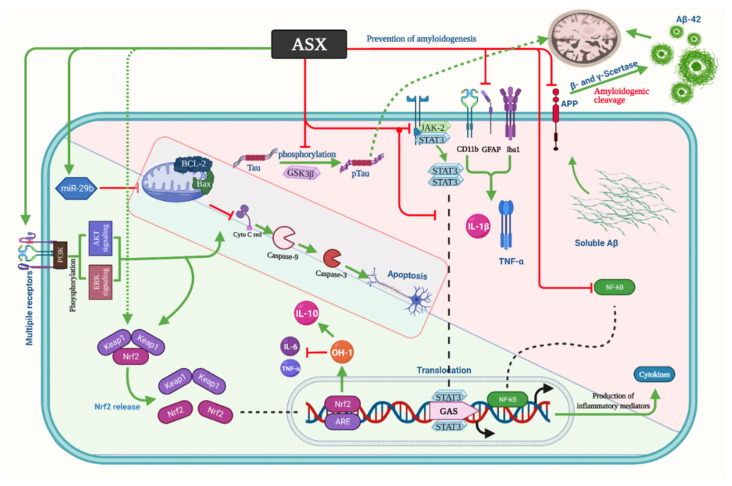
Figure 1.
Astaxanthin mechanism of action in Alzheimer’s disease. Aβ: Amyloid beta, APP: β-amyloid precursor protein, ASX: Astaxanthin, NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B, TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha, IL: Interleukin, Iba1: Ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1, GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein, STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, JAK2: Janus Kinase 2, GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta, p-Tau: Phosphorylated tau, Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma 2, Bax: Bcl-2-associated X protein, Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2, GAS: Glyoxylate, anapleurotic and succinyl CoA, OH: Hydroxide, Keap1: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1, Akt: Protein kinase B.