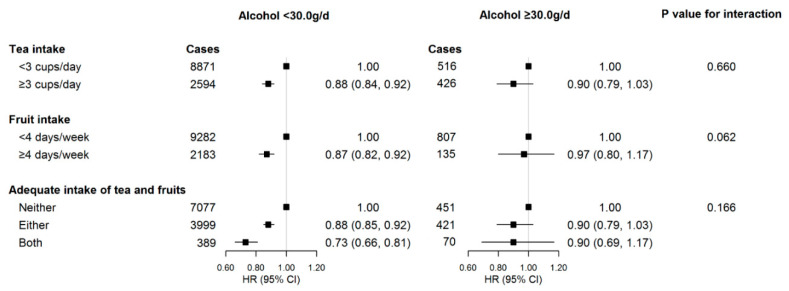
Figure 1.
Subgroup analyses of the associations between adequate intake of tea and fruits and risk of kidney stones according to the amount of alcohol consumed (n = 502,621). Abbreviations: HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval. Adjusted covariates were the same as those in model 3 of Table 2, as appropriate. Adequate intake was defined as tea consumption ≥3 cups/day or fruit consumption ≥4 days/week. Solid squares represent point estimates, and horizontal lines represent 95% confidence intervals.