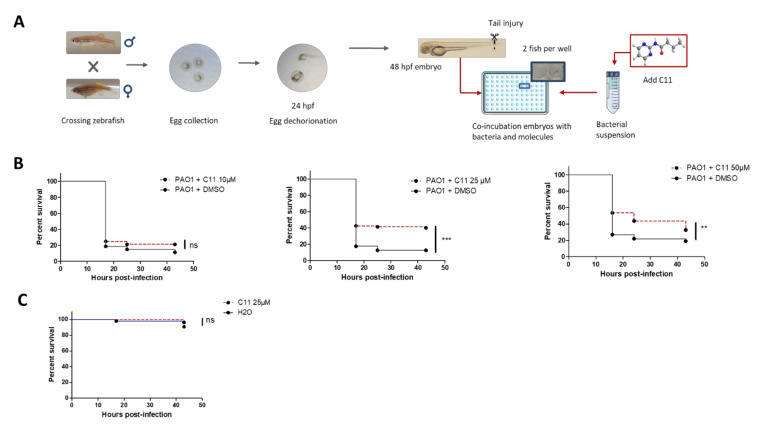
Figure 4.
Use of bath infection model to validate novel anti-Pseudomonas molecules such as C11 molecule (targeting quorum sensing). (A) Schematic protocol for testing antivirulence molecules in embryos bath infected with P. aeruginosa. Antivirulence molecules, which do not reduce bacterial viability outside the host, are added together with bacteria. (B) The antivirulence efficacy of C11 (dissolved in DMSO) was tested with embryos injured in the tail fin and bath infected with PAO1 suspension at approximately 107 CFU/mL in presence of C11 at 10, 25, or 50 µM. Injured embryos in the control group were treated with PAO1 suspension in presence of DMSO at 0.05, 0.13, or 0.25% (reflecting the amount of DMSO in the C11-treated groups). A significant difference (** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001) is found in the survival curve of C11-treated embryos compared to non-treated embryos at 25 or 50 µM. (C) The toxicity of C11 at 25 µM was monitored after immersion of embryos injured in the tail fin. For all experiments, the embryo survival was monitored for 45 hours and survival curves were represented with a Kaplan–Meier representation. Graphs represent the pool of three independent experiments (n = 60 larvae in total per condition).