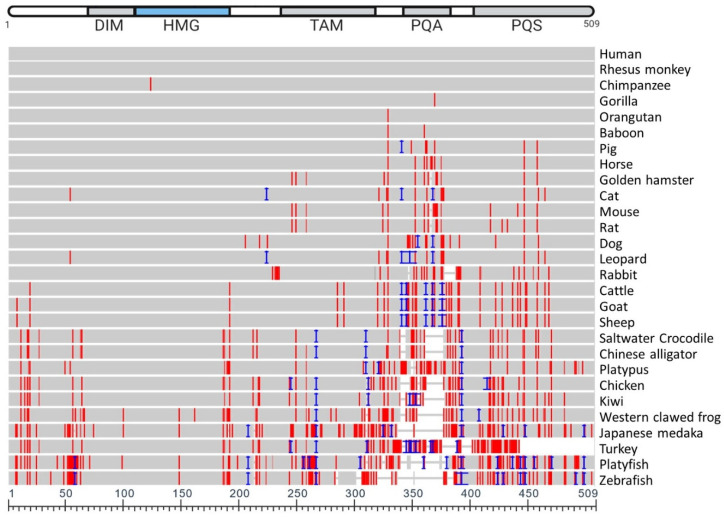
Figure 4.
Multiple sequence alignment of SOX9 amino acid sequences across 28 species, compared to human SOX9 reference. Human SOX9 protein along the top of the multiple sequence alignment, indicating the dimerization domain (DIM), DNA-binding HMG-box, transactivating domain in the middle of the protein (TAM), the proline, glutamine, and alanine rich region (PQA) and the proline, glutamine, and serine rich region (PQS). In the multiple sequence alignment, grey indicates identical sequence to human SOX9 at each residue, red indicates different residue, and blue indicates an insertion. Images created through NCBI COBALT (Constraint-based multiple alignment tool) with 28 sequences selected through the NCBI Orthologues feature, NCBI Multiple Alignment Sequence Alignment Viewer, Version 1.19.1 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/6662 (accessed on 16 February 2021)).