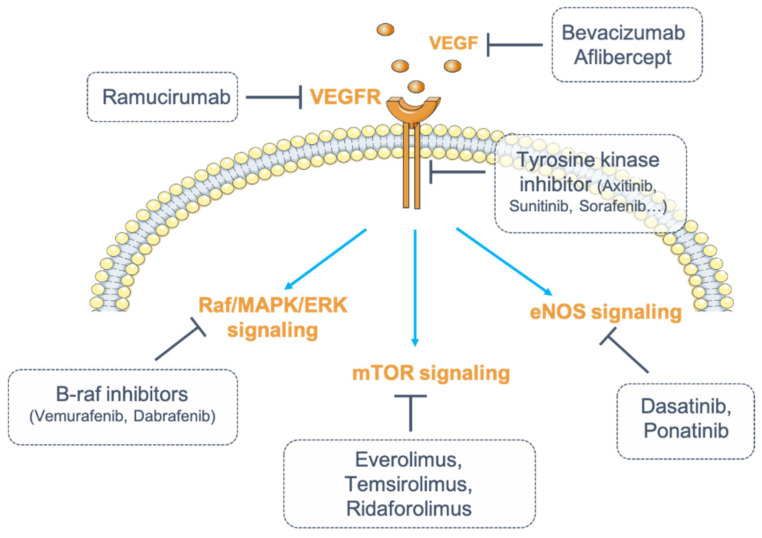
Figure 1.
Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) signaling. Numerous strategies exist to inhibit VEGF/VEGFR signaling. VEGF can be blocked by monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) (bevacizumab) or by fusion proteins (aflibercept). Its receptor, VEGFR, can be targeted by fully humanized monoclonal antibodies (ramucirumab). The receptor can also be targeted for its intracellular tyrosine kinase activity (tyrosine kinase inhibitors, TKIs). Finally, one strategy consists of inhibiting the downstream signaling pathways of VEGFR by targeting either the Raf (Rapidly Accelerated Fibrosarcoma)/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/ERK (Extracellular signal-Regulated Kinase) pathway with B-Raf inhibitors (dabrafenib, vemurafenib), or the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) pathway (dasatinib, ponatinib) or the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway (everolimus, temsirolimus, ridaforolimus).