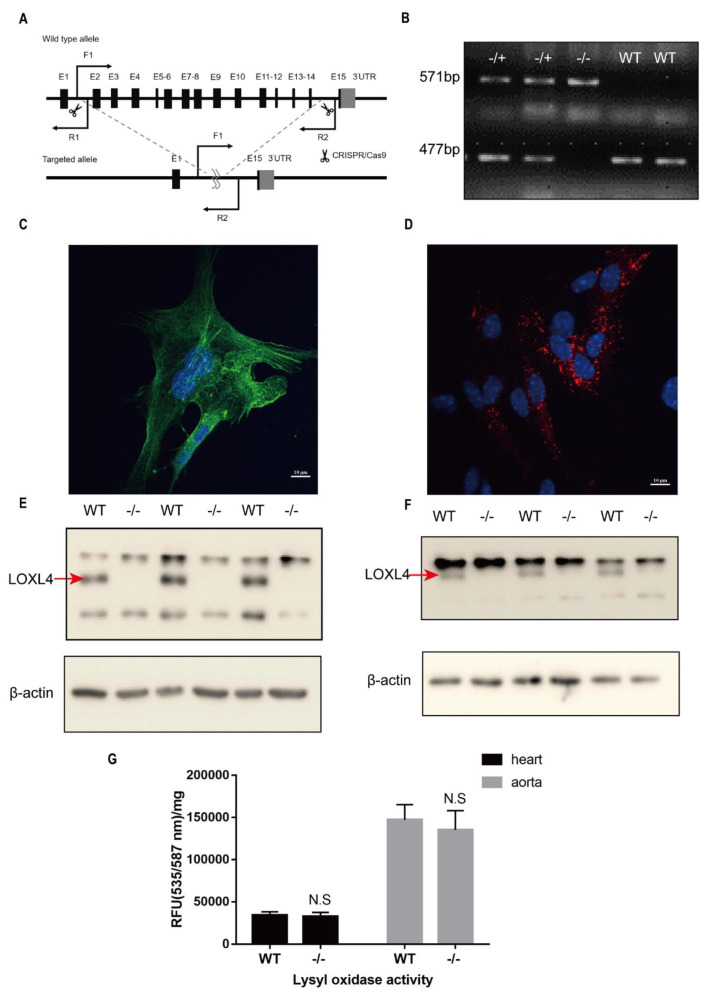
Figure 2.
Verification of the deletion of Loxl4 in mice and measurements of the lysyl oxidase activity of hearts and aortas. (A) The scheme of Loxl4 knockout strategy. Exons 2~14 were targeted to be deleted by CRISPR/Cas9 technology. F1, R1, and R2 indicate the locations of the primers used for genotyping. (B) Verification of Loxl4 deletion from genomic level. The lower bands were amplified with primers F1 and R1 (477 bp). These bands can only be amplified in wild-type or heterozygous mice and cannot be amplified in homozygous mice because of the absence of the sequence of primer R1. The upper bands were amplified with primers F1 and R2 (571 bp). These bands can only be amplified in heterozygous and homozygous mice, for the sequence between F1 and R2 is too long to be amplified in wild-type mice. (C) Immunostaining of actin (green) on aorta smooth muscle cells and (D) von Willebrand factor (Vwf) (red) on heart endothelial cells. Pictures were taken at a magnification of 100×. The bar is 10 µm. (E) Verification of Loxl4 deletion at the protein level in aorta smooth muscle cells and (F) heart endothelial cells. An about 70 kDa specific LOXL4 band was detected in wide-type mice but not in homozygous mice. (G) Lysyl oxidase activity of wild-type (n = 6) and Loxl4 knockout (KO) mice (n = 7) was evaluated by fluorescence (RFU) values per protein quantity (mg). p = 0.5354 and 0.3165 in hearts and aortas, respectively. WT, wild-type; −/+, heterozygote; −/−, KO; N.S, no significance.