FIG 4. IL-1β-KO blocked RV-induced development of an asthma-like phenotype and innate cytokine expression in immature mice.
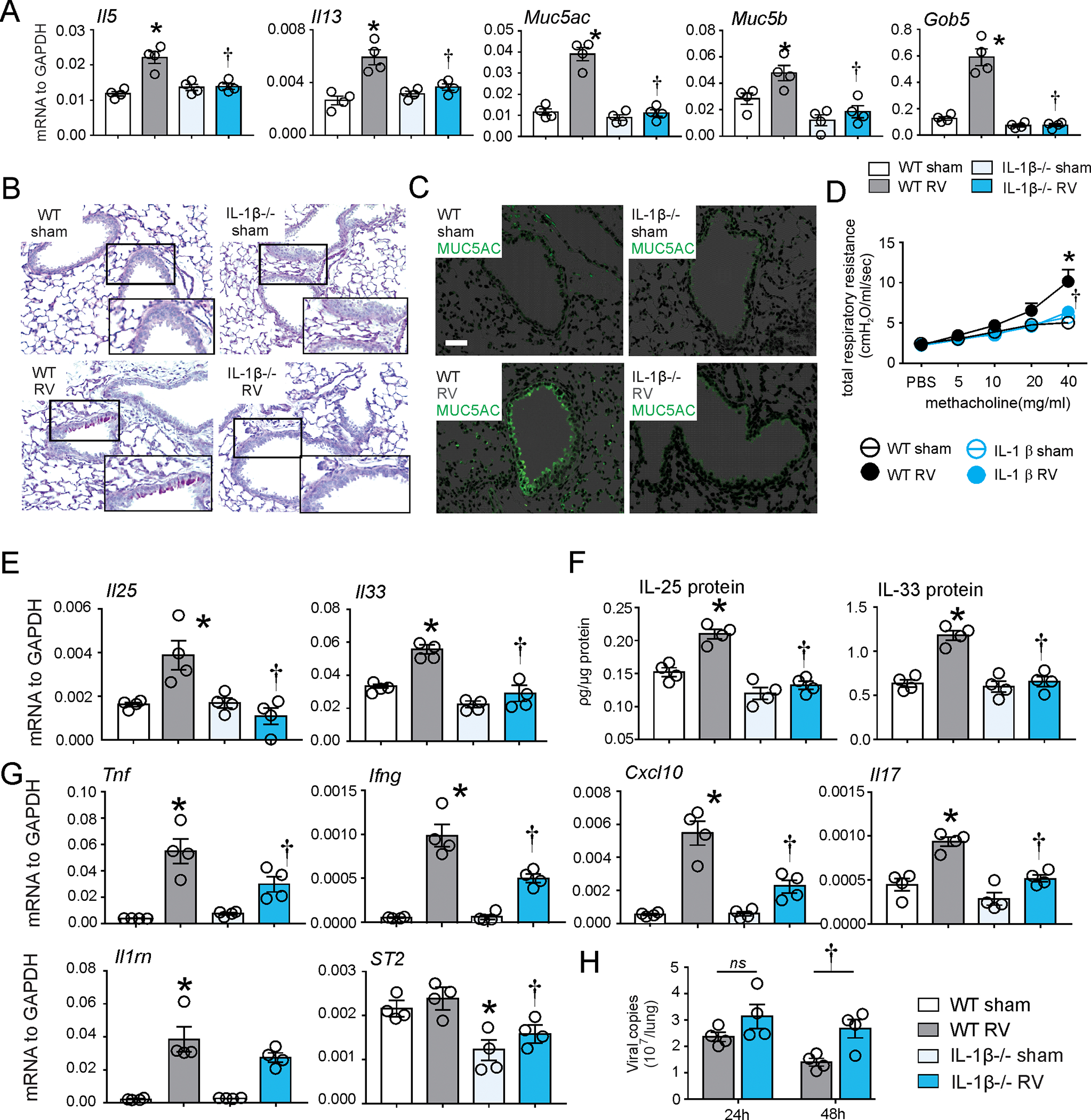
6-day old wild type C57BL/6 and IL-1β−/− mice were inoculated with sham or RV. A. Lung mRNA expression was measured 7 d post infection. (n = 4, mean±SEM, *different from WT sham, †different from WT RV, p<0.05, one-way ANOVA). Mucous metaplasia was assessed by PAS staining (B) and Muc5ac immunofluorescence (C). Lung sections prepared 3 wk after treatment of 6-d-old mice. D, Airway responsiveness of four wk-old baby mice, 21 d after sham and RV infection (n = 4, mean±SEM, *different from WT sham, †different from WT RV, p<0.05, two-way ANOVA). E, F. Whole-lung IL-25 and IL-33 mRNA and protein expression were examined seven and one day post-infection, respectively. G. Il1rl1, Il1rn, Ifng, Tnf, Il17 and Cxcl10 mRNA were examined one day post-infection. H. RV positive-strand RNA was assessed 24 h and 48 h after infection, and presented as viral copy number in total lung (n =4, mean±SEM, *different from WT sham, †different from WT RV, p<0.05, one-way ANOVA).
