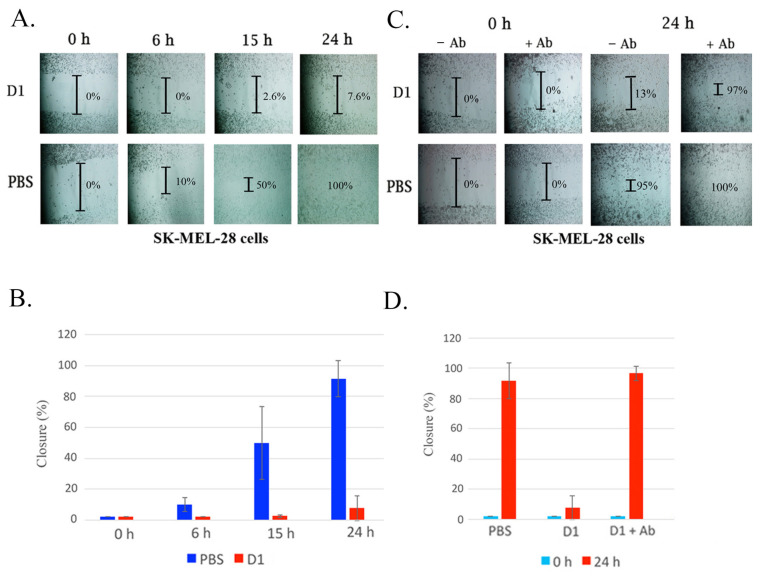
Figure 3.
Characterization and neutralization of D1 on cell migration using wound healing analysis. (A) A confluent monolayer of cells was maintained in the medium with an insert generating a wound. Inhibition of SK-MEL-28 cell migration was measured when the disintegrin was added to tissue culture media. SK-MEL-28 cell lines were incubated with D1 (0.5 mg/mL) for 24 h. Cells were allowed to migrate and were monitored at 0 h, 6 h, 15 h, and 24 h at 37 °C. Untreated cells with PBS were used as a control. Results are expressed as cell closure percentage relative to the PBS control, ± SD (n = 3). The extent of wound closure was quantified by multiple measurements of the width of the scratched area. (B) Quantification of inhibition of cell migration by snake venom a disintegrins. (C) Wound healing analysis using anti-disintegrin to neutralize the inhibition of cell migration of SK-MEL-28 cells was measured when the disintegrin was mixed with anti-disintegrin antibody and added to tissue culture media. A confluent monolayer of cells was maintained in the medium with an insert to leave a wound. The cultures were allowed to migrate for 24 h at 37 °C in the presence of disintegrin and disintegrins mixed with anti-disintegrin antibody. D1 (0.5 mg/mL) was pre-incubated with anti-disintegrin for 30 min. The samples were then added to SK-MEL-28 cells and incubated for 24 h. The extent of wound closure was quantified by multiple measurements as described in (A). (D) Quantification of inhibition of disintegrin activity by anti-disintegrin. Results are expressed as cell closure percentage relative to the PBS control, ± SD (n = 3).