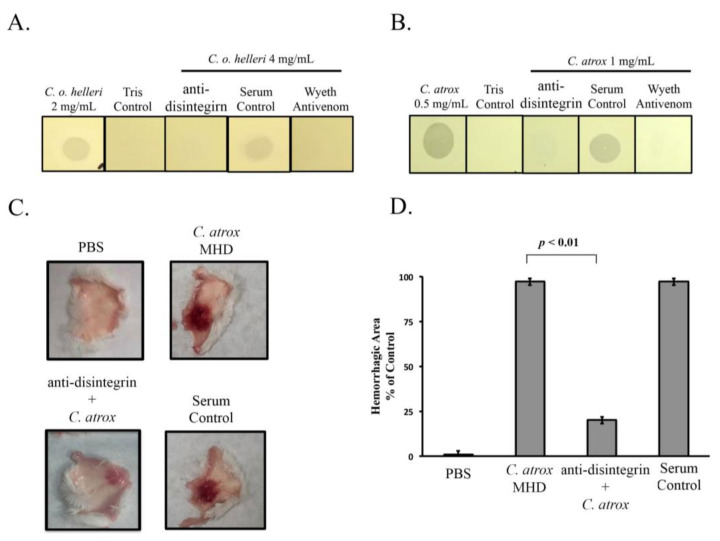
Figure 7.
Neutralization of snake venom using anti-disintegrin. (A) Proteolytic neutralization of C. o. helleri venom using anti-disintegrin. A 2MGD of C. o. helleri venom was incubated for 30 min with serum control, anti-disintegrin or Antivenin Polyvalent (Wyeth) antivenom at equal volumes and then 20 µL of sample were applied onto the gelatin film and incubated for 4 h. (B) Proteolytic neutralization of C. atrox venom using anti-disintegrin. A 2MGD of C. atrox venom was incubated for 30 min with serum control, anti-disintegrin or Antivenin Polyvalent (Wyeth) antivenom at equal volumes and then 20 µL of sample were applied onto the gelatin film and incubated for 4 h. (C) Neutralization of hemorrhagic activity by anti-disintegrin. A total of 0.1 mL of MHD of C. atrox venom or venom/anti-disintegrin mixture was injected subdermally into the abdomen of BALB/c mice. After 24 h, the mice were sacrificed, and the skin removed for measurement of hemorrhagic area. The controls consisted of PBS, serum control, and MHD. An MHD contained 2.5 µg of venom protein capable of producing a 10 mm hemorrhagic spot. (D) Hemorrhagic activity was quantified by densitometry and is expressed as the hemorrhagic area percentage relative to the PBS control, ± SD (n = 3).