Figure 2. The AHR pathway overlaps TCF21 downstream pathways and is enriched in open chromatin regions in HCASMC.
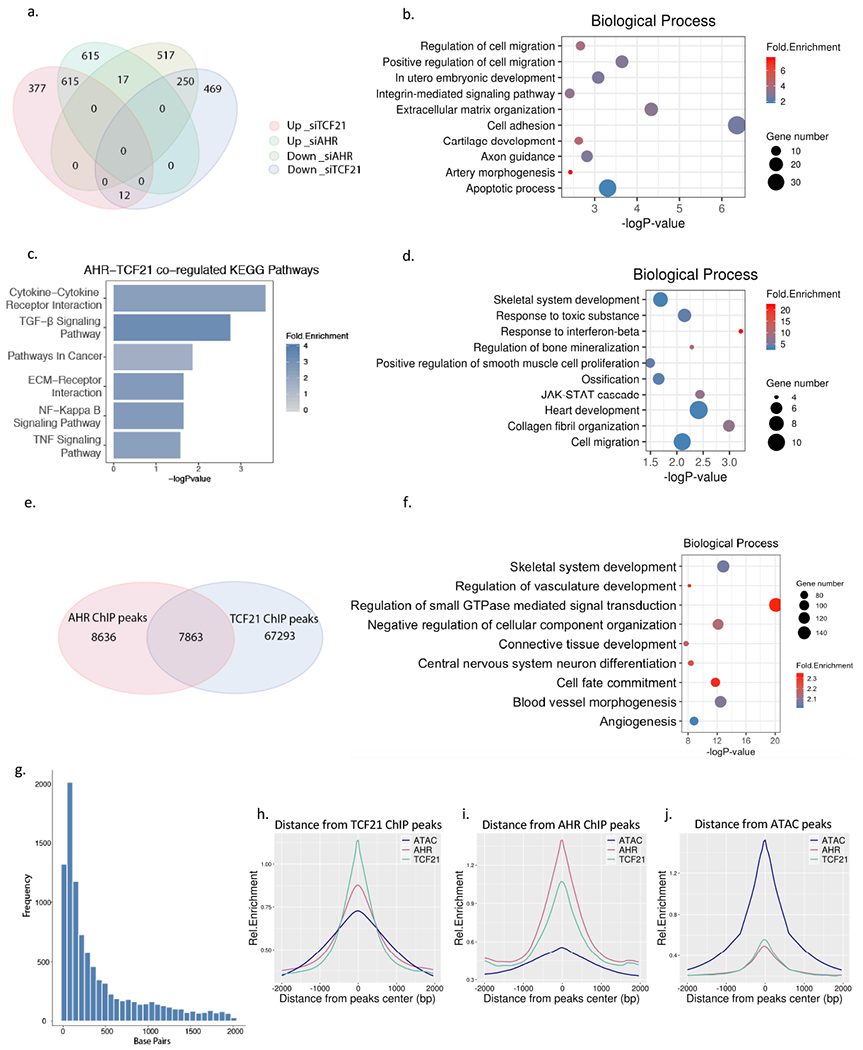
(a) Comparison of AHR knockdown RNA-Seq and TCF21 knockdown RNA-Seq results from HCASMC. A total of 1004 genes were up-reguated and 814 genes down-regulated in AHR KD, 1247 genes up-regulated, and 731 genes down-regulated in TCF21 KD (FDR <0.00001, Fold Change >1.3). Among these 615 up-regulated and 250 down-regulated genes overlapped between the AHR KD and TCF21 KD groups, respectively (Hypergeometric test p =1e-4642) (b) Top enriched biological pathways from up-regulated genes that are common to AHR KD and TCF21 KD (c) The top KEGG pathways enriched from genes regulated by both TCF21 and AHR. (d) Top enriched biological pathways unique to AHR KD. (e) AHR ChIP-Seq and TCF21 ChIP-Seq target loci share a significant number of intersected peaks. (f) DAVID Gene Ontology analysis of overlapping AHR and TCF21 binding peak genes identified by GREAT. (g) The distance between the AHR and TCF21 binding sites are on average 50-100 bp apart. (h-j) The peaks of TCF21 ChIP-Seq (green line), AHR ChIP-Seq (red line) and AHR overexpression ATAC-seq peaks (blue line) co-localize genome-wide, as shown by overlapping relative enrichment centered around each respective coordinates.
