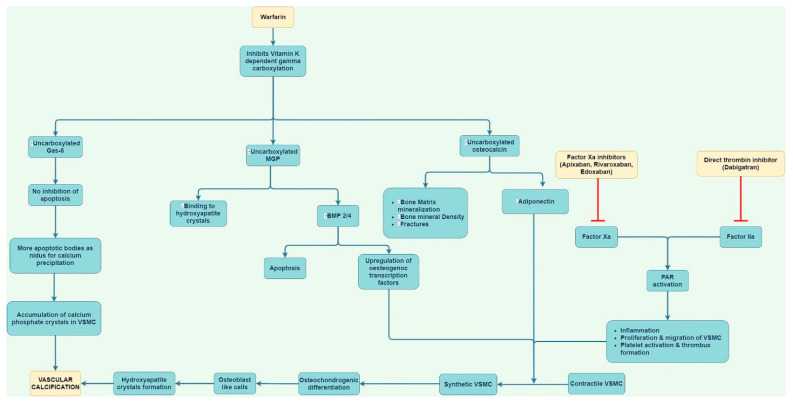
Figure 2.
Summary figure showing mechanism and implication of warfarin and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) on vascular calcification. Warfarin causes calcification due to inhibition of vitamin-K-dependent carboxylation. DOACs may prevent calcification by inhibiting protease-activated receptors (PAR) activation. Gas-6 = growth arrest specific 6 protein; VSMC = vascular smooth muscle cells; MGP = matrix gla protein; BMP = bone morphogenetic protein.