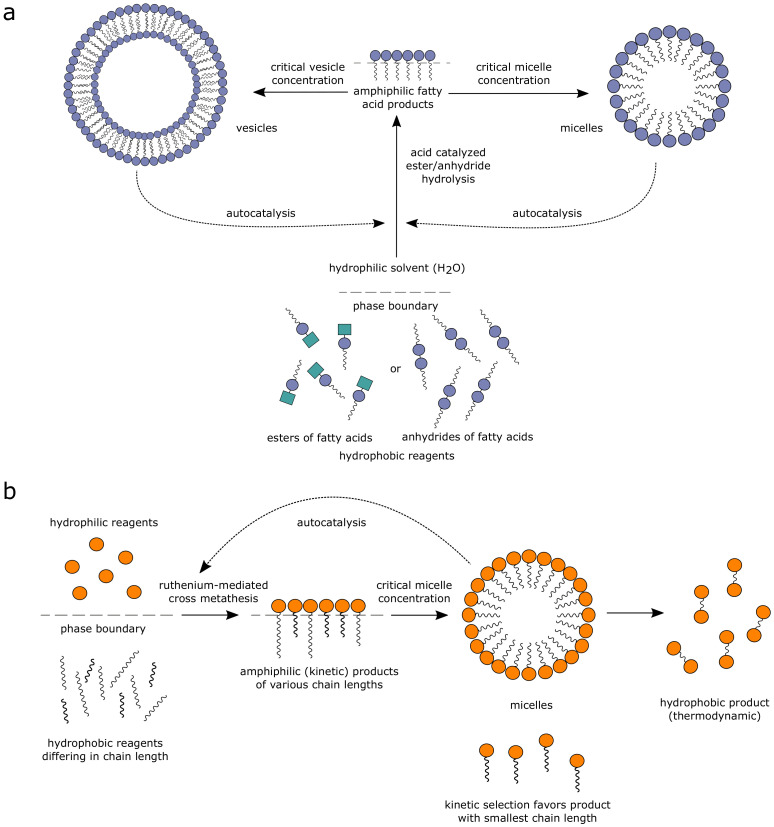
Figure 3.
Lipid-based autocatalytic systems. (a) Schematic representation of the self-assembly of ester or anhydrides of fatty acid molecules into micelles. Here, micelles catalyze the production of more micelles by enhancing the solubility of the substrates in aqueous phase [94]. Such a process can also lead to the formation of vesicles from the heterogenous mixture of protonated and non-protonated fatty-acid molecules. Similar to micelles, these vesicles can also lead to the production of more vesicles, making the process autocatalytic [95]. (b) Another self-assembly system based on lipids in which amphiphilic substrates are generated in situ, employing metathesis reactions between hydrophobic and hydrophilic alkenes. Similar to (a), these substrates assemble to form micelles in an autocatalytic manner, but in this case, the starting material is a mixture of heterogenous substrates of varying chain-lengths [102]. This system demonstrates the enrichment of only one type of amphiphile through miceller autucatalysis, raising the possibility of selection in the lipid-based self-reproducing system (figure adapted from [102]).