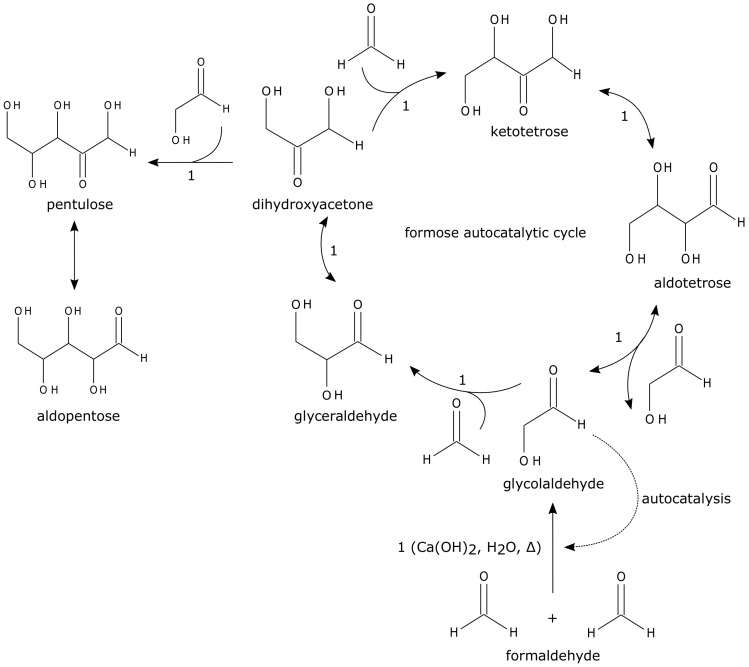
Figure 5.
Sugar-based (formose) autocatalytic system. Schematic representation of the autocatalytic system based on the formose reaction. Here, the autocatalytic cycle starts from condensation of two formaldehyde molecules (one carbon each) to form glycolaldehyde (two carbon), which further leads to the formation of higher carbon sugar molecules [115,117]. The reaction is facilitated by basic conditions (1. Ca(OH)2, H2O, and Δ) and product of the reaction (glycolaldehyde). In addition to the autocatalytic cycle, side reactions lead to many higher products (for example, aldopentose) (figure adapted from [123]).