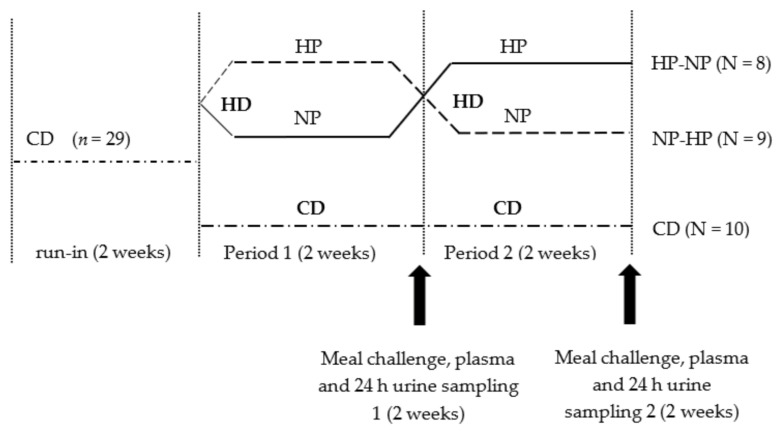
Figure 1.
Study design. All participants started on a two-week run-in period on a weight maintaining control diet (CD, 27.8 En% fat; 16.9 En% protein; 55.3 En% carbohydrate). Thereafter, participants were randomly assigned to either the high-fat-hypercaloric diet group (HD; n = 19) or to the reference group consuming a control diet (CD; n = 10) for the following 4 weeks of intervention. Participants in the HD-group were overfed with 2 MJ per day. The HD intervention consisted of a of a 2 × 2-week cross-over design with two separate periods: a 2-week high-protein intervention (HP, 37.7 En% fat; 25.7 En% protein; 36.6 En% carbohydrates) and a 2-week normal-protein intervention (NP; 39.4 En% fat; 15.4 En% protein; 45.2 En% carbohydrates). We collected 24 h urine samples at the end of periods 1 and 2, a meal challenge with blood sampling was performed after period 1 and 2. HD—high-fat hypercaloric diet; CD—control diet; HP—high protein condition (within high-fat hypercaloric diet); NP, normal protein condition (within high-fat hypercaloric diet).