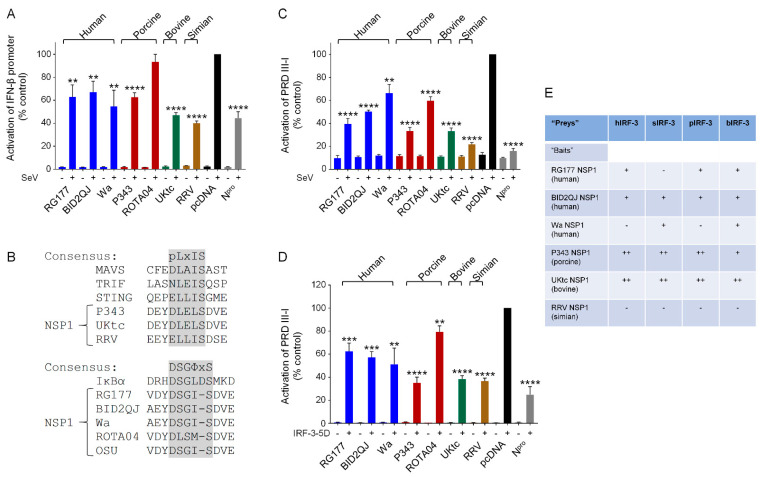
Figure 1.
NSP1 (non-structural protein) from human and animal rotavirus strains inhibit interferon (IFN)-β induction by IFN regulatory factor (IRF)-3. (A,C,D) Human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293 cells were transfected with a plasmid containing a firefly luciferase gene under the control of the IFN-β promoter (A) or the PRDIII-I element from the IFN-β promoter (C,D), a plasmid directing constitutive expression of renilla luciferase as an internal control, and either the empty vector pcDNA3.1, or pcDNA3.1 encoding the NSP1 protein from human (RG177, BID2QJ, Wa), porcine (P343, ROTA04), bovine (UKtc) or simian (RRV) group A rotavirus (RVA) strains, or classical swine fever virus (CSFV) Npro as a positive control. Reporter genes were activated by infection with Sendai virus (SeV) at 24 h post-transfection (A,C), or inclusion of a plasmid encoding constitutively active IRF-3 (IRF-3-5D) in the transfection (D). 48 h after transfection, cells were lysed and levels of firefly and renilla luciferase were measured. The normalized activity of the reporter gene in the samples transfected with the empty vector and induced by SeV (A,C) or IRF-3-5D (D) was set to 100%. Differences between induced samples containing NSP1 or Npro and the induced control sample containing the empty vector were assessed using the Student’s t-test (** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001). (B) Sequences of the C-terminal motifs present in different NSP1s. P343, UKtc, and RRV NSP1s contain a pLxIS motif (where p represents a hydrophilic residue and x is any amino acid) similar to the IRF-3 binding sites present in mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS), TRIF, and STING. RG177, BID2QJ, Wa, and OSU NSP1s contain a DSGΦxS motif similar to that found in IκB (where Φ represents a hydrophobic residue and x is any or no amino acid). (E) Yeast transformed with plasmids encoding the NSP1 proteins from various RVA strains as “baits” and plasmids encoding human (h), simian (s), porcine (p), or bovine (b) IRF-3 as “preys” were streaked onto triple drop-out (TDO) and quadruple drop-out (QDO) media to assay for protein-protein interactions. ‘+’ indicates growth on TDO media but no growth on QDO media, ‘++’ indicates growth on QDO media, and ‘−‘ indicates no growth on either selection medium (i.e., no interaction).