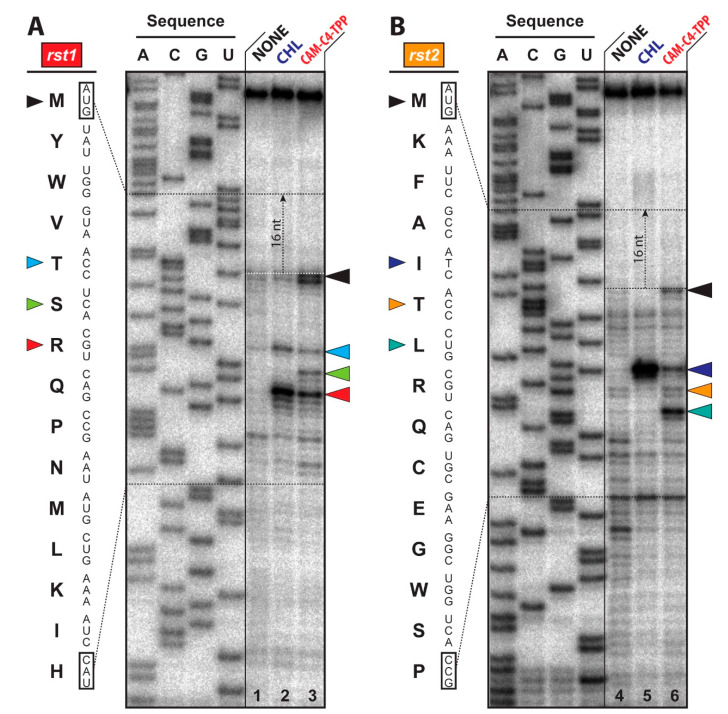
Figure 6.
CAM-C4-TPP is capable of arresting translation at the start codon. Ribosome stalling by CAM-C4-TPP on rst1 (A) and rst2 (B) mRNAs in comparison with CHL, as revealed by reverse-transcription primer-extension inhibition (toe-printing) assay in a cell-free translation system. Nucleotide sequences of rst1 and rst2 mRNAs and their corresponding amino acid sequences are shown on the left. Black arrowheads mark translation arrest at the start codon, while variously colored arrowheads point to the drug-induced arrest sites within the coding sequences of each of the two used mRNAs. Note that, due to the large size of the ribosome, the reverse transcriptase used in the toe-printing assay stops 16 nucleotides downstream of the codon located in the P-site.