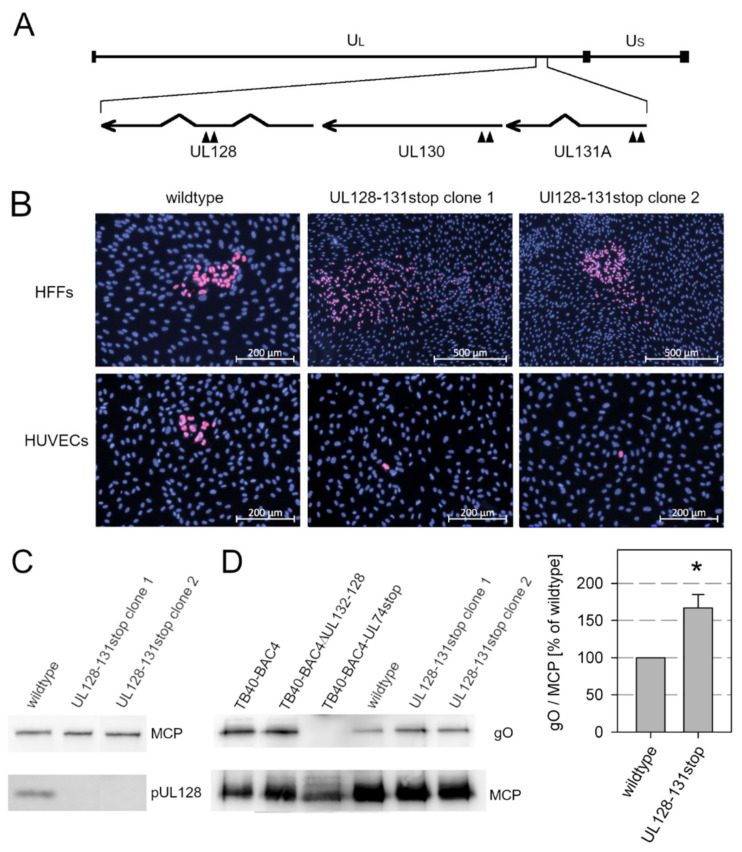
Figure 2.
Effect of stop mutations in viral genes encoding for the accessory proteins of the pentamer complex. (A) Schematic representation of the viral genome with the unique long and the unique short section indicated by UL and US, respectively. The UL128 gene locus is shown enlarged below the genome map, and the positions of the stop codons that were introduced into the open reading frames of UL128, UL130, and UL131A are indicated by arrow heads. (B) Virus reconstituted in HFFFtet cells from wildtype Merlin pAL1502 or mutant genomes was used to infect fibroblasts (HFFs) which were then cocultured with an excess of uninfected HFFs or endothelial cells (HUVECs) for 5 d. After the incubation time, cultures were fixed and immunostained for viral immediate early (IE) antigen. (C) Lysates of infected HFFs were analyzed by separation on a 10% polyacrylamide gel under reducing conditions and subsequent immunoblotting with antibodies against pUL128 to test whether the knockout of UL128 was successful. The major capsid protein (MCP) was detected as a loading control. (D) Virus particles were prepared from infected HFFs (TB40-BAC4 and derivatives) or HFFFtet cells (Merlin pAL1502 wildtype and UL128-131stop mutants) by gradient purification and lysed. Lysates were separated on a 10% polyacrylamide gel under nonreducing conditions and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against glycoprotein O (gO) or MCP (loading control). For Merlin wildtype and mutants, the ratio of gO/MCP signals were determined to evaluate the effect of the knockout of the UL128 locus genes on the incorporation of gO into virion particles. Bars indicate mean values of four replicates with wildtype (two blots of two independent preparations) and eight replicates of UL128-131stop (two blots of two independent preparations of each of the two clones). Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). The asterisk indicates a significant difference as compared with wildtype (*, p < 0.05).