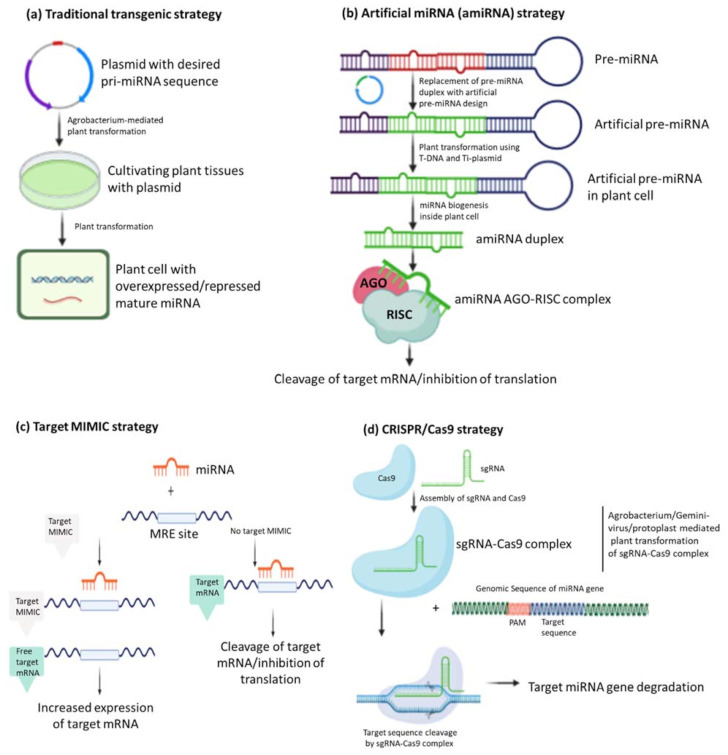
Figure 3.
Overview of miRNA-based strategies for crop improvement. Illustrating (a) the traditional transgenic approach targeting directly primary-miRNA (pri-miRNA) in plants; (b) the artificial miRNA (amiRNA) strategy to enhance or repress miRNA expression in plants (Sablok et al., 2011). The amiRNA is designed to have a complementary sequence to the target mRNA and stem-loop structure like the original miRNA. The amiRNA then transfers into the plant cell using traditional transformation techniques, where its biogenesis occurs like original miRNA. Finally, amiRNA targets the mRNA without affecting non-target genes; (c) target MIMIC strategy where target MIMIC instead of target mRNA is recognized by miRNA; (MRE site: miRNA recognition site) [194]; (d) miRNA-targeting CRISPR/Cas9 approach to manipulate the miRNA gene using sgRNA-Cas9 complex. CRISPR/Cas9 techniques based on two components, (i) sgRNA: single guide RNA, and (ii) Cas9 endonucleases. The sgRNA consists of a 20-nt-long spacer sequence which is highly specific to target DNA having a 5’-NGG-3’PAM (protospacer adjacent motif). The Cas9 vector construct and sgRNA complex transfer into a plant cell using a transformation technique. In the plant cell, sgRNA-Cas9 complex target and cleave the DNA and degrade the targeted gene. This figure was created with the BioRender app (https://app.biorender.com/; accessed on 30 April 2020).