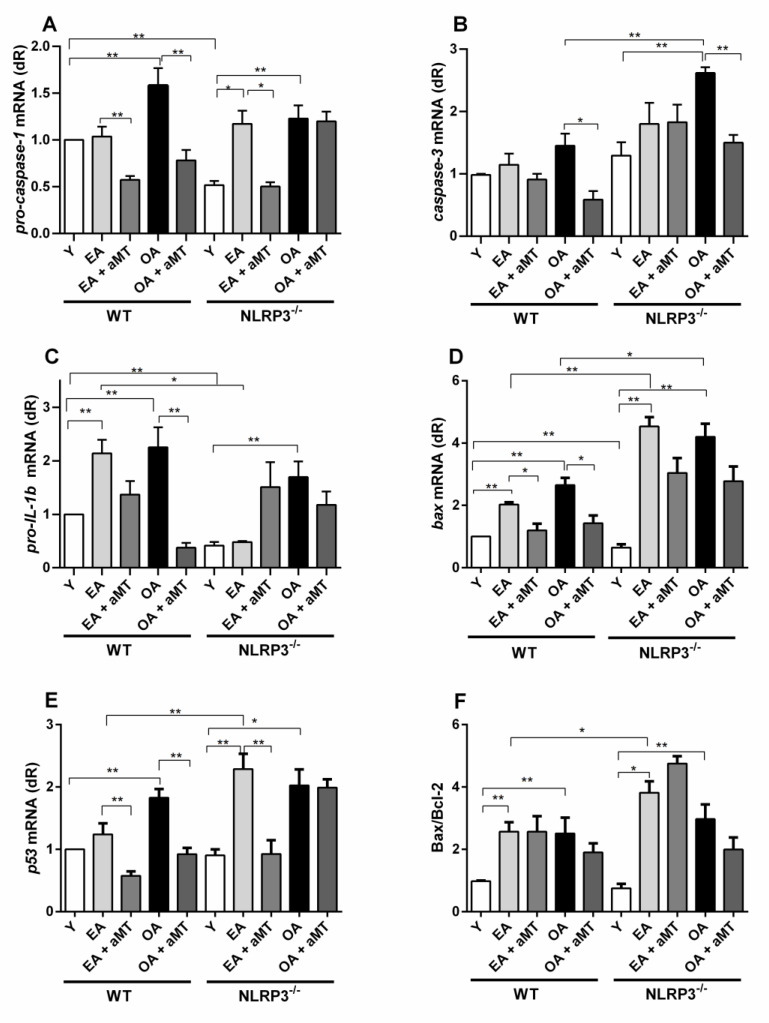
Figure 2.
Changes in mRNA expression of the molecular inflammatory and apoptosis parameters in WT and NLRP3− during aging and melatonin supplementation. Experiments were performed in gastrocnemius muscle of young (Y), early aged (EA), early aged with melatonin (EA + aMT), old-aged (OA), and old-aged with melatonin (OA + aMT) of wild type (WT) and NLRP3− mice. Following mRNA expression levels were measured by qRT-PCR analysis: A-pro-caspase-1, B-caspase-3, C-pro-IL-1β, D-Bax, E-p53, and F-ratio Bax/Bcl-2. Increased pro-caspase-1, pro-IL-1β, bax, p53 levels and Bax/Bcl-2 ratio with age in WT animals, were contrarested by melatonin administration in all parameters, except Bax/Bcl-2 (A,C–E). Aging afected the expression of all molecular parameters in NLRP3- animals (A–F), although the levels of pro-caspase-1, pro-IL-1β and bax were lower in early aged mutant animals compared to the WT ones of the same age (A,C,D). Melatonin administration decreased pro-caspase-1 and p53 expression in EA NLRP3- group (A,E), as well as reduced caspase-3 levels in OA mutant mice (B). Data are expressed as means ± SEM (n = 5 animals/group). Comparisons between groups are indicated in the graphs. * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01.