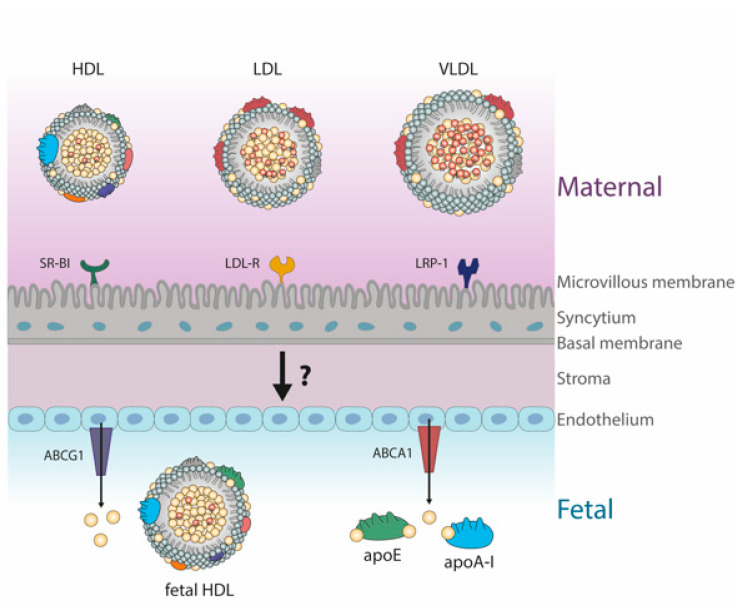
Figure 1.
Described routes how maternal cholesterol is transported across the human placenta. First, maternally derived lipoproteins interact with respective receptors at the microvillous membrane of the syncytium. After uptake of cholesterol in the syncytium, it is secreted/effluxed to lipid-poor acceptor apolipoproteins of fetal HDL. How stroma transfers cholesterol to the fetoplacental endothelium remains elusive. High-density lipoprotein; SR-BI; scavenger receptor BI; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; VLDL, very-low-density lipoprotein; LDL-R, low-density lipoprotein receptor; LRP-1, LDL receptor-related protein 1; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette A1; ABCG1, ATP-binding cassette G1.