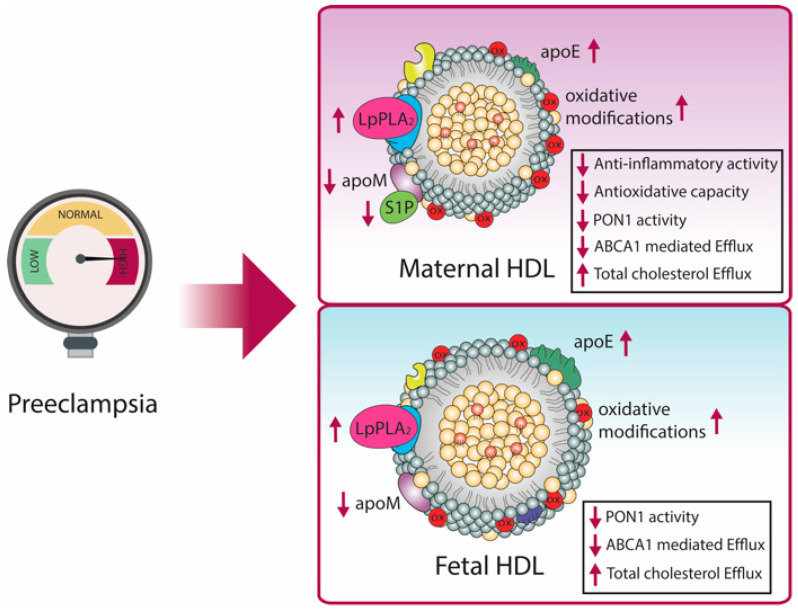
Figure 3.
PE affects maternal and fetal HDL composition and function. Changes are indicated with purple arrows. In maternal HDL, a decrease in PON1 activity, apoM, and S1P content was observed, whereas apoE and LpPLA2 were increased. These changes in HDL composition were associated with reduced anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activity, but increased cholesterol efflux capacity. Fetal HDL of PE pregnancies showed similar changes, with reduced PON1 activity and apoM, but increased LpPLA2 and apoE, accompanied by increased cholesterol efflux capacity. Oxidative modifications of lipids were detected in both maternal and fetal HDL. HDL, high-density lipoprotein; apo, apolipoprotein; PON1, paraoxonase 1; LpPLA2, lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2.